Page 201 - Veterinary Histology of Domestic Mammals and Birds, 5th Edition
P. 201
Digestive system (apparatus digestorius) 183
thickened rostrally to form the dental pad (pulvinus den- longitudinally oriented sheets of collagen fibres and the
VetBooks.ir tale). The stratified squamous epithelium of the dental pad is skeletal muscles of the soft palate (m. palatinus, m. leva-
tor veli palatini and m. tensor veli palatini).
heavily cornified.
Soft palate (palatum molle, velum palatinum) Species variation
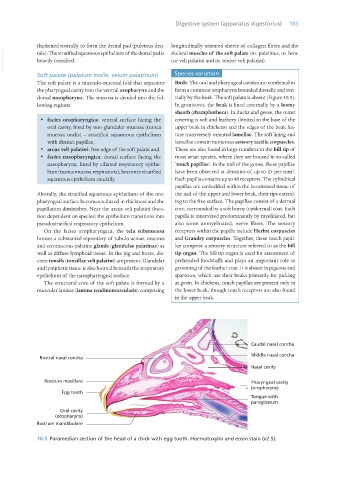
The soft palate is a musculo-mucosal fold that separates Birds: The oral and pharyngeal cavities are combined to
the pharyngeal cavity into the ventral oropharynx and the form a common oropharynx bounded dorsally and ven-
dorsal nasopharynx. The mucosa is divided into the fol- trally by the beak. The soft palate is absent (Figure 10.5).
lowing regions: In granivores, the beak is lined externally by a horny
sheath (rhamphotheca). In ducks and geese, the outer
· facies oropharyngica: ventral surface facing the covering is soft and leathery (limited to the base of the
oral cavity, lined by non-glandular mucosa (tunica upper beak in chickens) and the edges of the beak fea-
mucosa oralis) – stratified squamous epithelium ture transversely oriented lamellae. The soft lining and
with distinct papillae, lamellae contain numerous sensory tactile corpuscles.
· arcus veli palatini: free edge of the soft palate and These are also found in large numbers in the bill tip of
· facies nasopharyngica: dorsal surface facing the most avian species, where they are housed in so-called
nasopharynx, lined by ciliated respiratory epithe- ‘touch papillae’. In the nail of the goose, these papillae
2
lium (tunica mucosa respiratoria); becomes stratified have been observed at densities of up to 25 per mm .
squamous epithelium caudally. Each papilla contains up to 40 receptors. The cylindrical
papillae are embedded within the keratinised tissue of
Aborally, the stratified squamous epithelium of the oro- the nail of the upper and lower beak, their tips extend-
pharyngeal surface becomes reduced in thickness and the ing to the free surface. The papillae consist of a dermal
papillation diminishes. Near the arcus veli palatini (loca- core, surrounded by a soft horny (epidermal) coat. Each
tion dependent on species) the epithelium transitions into papilla is innervated predominantly by myelinated, but
pseudostratified respiratory epithelium. also some unmyelinated, nerve fibres. The sensory
On the facies oropharyngica, the tela submucosa receptors within the papilla include Herbst corpuscles
houses a substantial repository of tubulo-acinar, mucous and Grandry corpuscles. Together, these touch papil-
and seromucous palatine glands (glandulae palatinae) as lae comprise a sensory structure referred to as the bill
well as diffuse lymphoid tissue. In the pig and horse, dis- tip organ. The bill tip organ is used for assessment of
crete tonsils (tonsillae veli palatini) are present. Glandular prehended foodstuffs and plays an important role in
and lymphatic tissue is also located beneath the respiratory grooming of the feather coat. It is absent in pigeons and
epithelium of the nasopharyngeal surface. sparrows, which use their beaks primarily for picking
The structural core of the soft palate is formed by a at grain. In chickens, touch papillae are present only in
muscular lamina (lamina tendinomuscularis) comprising the lower beak, though touch receptors are also found
in the upper beak.
10.5 Paramedian section of the head of a chick with egg tooth. Haematoxylin and eosin stain (x2.5).
Vet Histology.indb 183 16/07/2019 15:00