Page 236 - Veterinary Histology of Domestic Mammals and Birds, 5th Edition
P. 236
218 Veterinary Histology of Domestic Mammals and Birds
VetBooks.ir
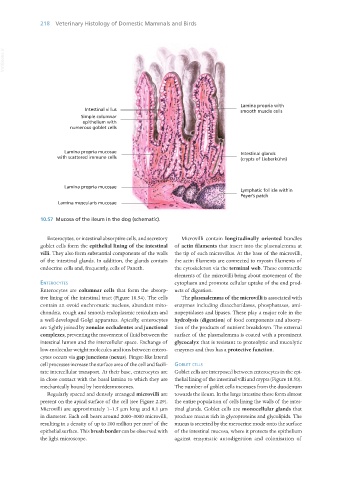
10.57 Mucosa of the ileum in the dog (schematic).
Enterocytes, or intestinal absorptive cells, and secretory Microvilli contain longitudinally oriented bundles
goblet cells form the epithelial lining of the intestinal of actin filaments that insert into the plasmalemma at
villi. They also form substantial components of the walls the tip of each microvillus. At the base of the microvilli,
of the intestinal glands. In addition, the glands contain the actin filaments are connected to myosin filaments of
endocrine cells and, frequently, cells of Paneth. the cytoskeleton via the terminal web. These contractile
elements of the microvilli bring about movement of the
enteRocytes cytoplasm and promote cellular uptake of the end prod-
Enterocytes are columnar cells that form the absorp- ucts of digestion.
tive lining of the intestinal tract (Figure 10.54). The cells The plasmalemma of the microvilli is associated with
contain an ovoid euchromatic nucleus, abundant mito- enzymes including disaccharidases, phosphatases, ami-
chondria, rough and smooth endoplasmic reticulum and nopeptidases and lipases. These play a major role in the
a well-developed Golgi apparatus. Apically, enterocytes hydrolysis (digestion) of food components and absorp-
are tightly joined by zonulae occludentes and junctional tion of the products of nutrient breakdown. The external
complexes, preventing the movement of fluid between the surface of the plasmalemma is coated with a prominent
intestinal lumen and the intercellular space. Exchange of glycocalyx that is resistant to proteolytic and mucolytic
low-molecular weight molecules and ions between entero- enzymes and thus has a protective function.
cytes occurs via gap junctions (nexus). Finger-like lateral
cell processes increase the surface area of the cell and facili- goblet cells
tate intercellular transport. At their base, enterocytes are Goblet cells are interposed between enterocytes in the epi-
in close contact with the basal lamina to which they are thelial lining of the intestinal villi and crypts (Figure 10.50).
mechanically bound by hemidesmosomes. The number of goblet cells increases from the duodenum
Regularly spaced and densely arranged microvilli are towards the ileum. In the large intestine these form almost
present on the apical surface of the cell (see Figure 2.29). the entire population of cells lining the walls of the intes-
Microvilli are approximately 1–1.5 μm long and 0.1 μm tinal glands. Goblet cells are monocellular glands that
in diameter. Each cell bears around 2000–3000 microvilli, produce mucus rich in glycoproteins and glycolipids. The
resulting in a density of up to 200 million per mm of the mucus is secreted by the merocrine mode onto the surface
2
epithelial surface. This brush border can be observed with of the intestinal mucosa, where it protects the epithelium
the light microscope. against enzymatic autodigestion and colonisation of
Vet Histology.indb 218 16/07/2019 15:01