Page 246 - Veterinary Histology of Domestic Mammals and Birds, 5th Edition
P. 246
228 Veterinary Histology of Domestic Mammals and Birds
VetBooks.ir
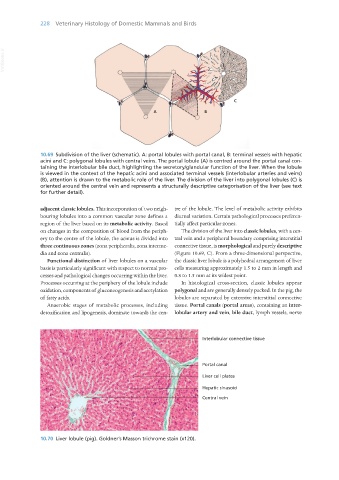
10.69 Subdivision of the liver (schematic). A: portal lobules with portal canal, B: terminal vessels with hepatic
acini and C: polygonal lobules with central veins. The portal lobule (A) is centred around the portal canal con-
taining the interlobular bile duct, highlighting the secretory/glandular function of the liver. When the lobule
is viewed in the context of the hepatic acini and associated terminal vessels (interlobular arteries and veins)
(B), attention is drawn to the metabolic role of the liver. The division of the liver into polygonal lobules (C) is
oriented around the central vein and represents a structurally descriptive categorisation of the liver (see text
for further detail).
adjacent classic lobules. This incorporation of two neigh- tre of the lobule. The level of metabolic activity exhibits
bouring lobules into a common vascular zone defines a diurnal variation. Certain pathological processes preferen-
region of the liver based on its metabolic activity. Based tially affect particular zones.
on changes in the composition of blood from the periph- The division of the liver into classic lobules, with a cen-
ery to the centre of the lobule, the acinus is divided into tral vein and a peripheral boundary comprising interstitial
three continuous zones (zona peripheralis, zona interme- connective tissue, is morphological and purely descriptive
dia and zona centralis). (Figure 10.69, C). From a three-dimensional perspective,
Functional distinction of liver lobules on a vascular the classic liver lobule is a polyhedral arrangement of liver
basis is particularly significant with respect to normal pro- cells measuring approximately 1.5 to 2 mm in length and
cesses and pathological changes occurring within the liver. 0.8 to 1.5 mm at its widest point.
Processes occurring at the periphery of the lobule include In histological cross-section, classic lobules appear
oxidation, components of gluconeogenesis and acetylation polygonal and are generally densely packed. In the pig, the
of fatty acids. lobules are separated by extensive interstitial connective
Anaerobic stages of metabolic processes, including tissue. Portal canals (portal areas), containing an inter-
detoxification and lipogenesis, dominate towards the cen- lobular artery and vein, bile duct, lymph vessels, nerve
Interlobular connective tissue
Portal canal
Liver cell plates
Hepatic sinusoid
Central vein
10.70 Liver lobule (pig). Goldner’s Masson trichrome stain (x120).
Vet Histology.indb 228 16/07/2019 15:02