Page 247 - Veterinary Histology of Domestic Mammals and Birds, 5th Edition
P. 247
Digestive system (apparatus digestorius) 229
VetBooks.ir
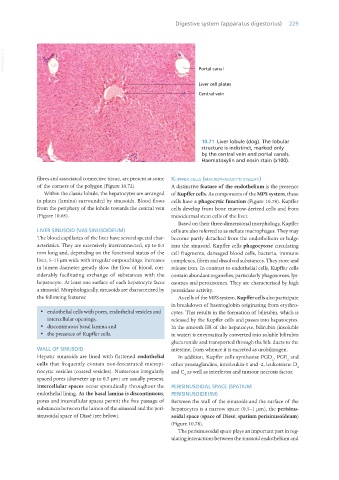
10.71 Liver lobule (dog). The lobular
structure is indistinct, marked only
by the central vein and portal canals.
Haematoxylin and eosin stain (x100).
fibres and associated connective tissue, are present at some kuPffeR cells (macRoPhagocyti stellati)
of the corners of the polygon (Figure 10.72). A distinctive feature of the endothelium is the presence
Within the classic lobule, the hepatocytes are arranged of Kupffer cells. As components of the MPS system, these
in plates (lamina) surrounded by sinusoids. Blood flows cells have a phagocytic function (Figure 10.78). Kupffer
from the periphery of the lobule towards the central vein cells develop from bone marrow-derived cells and from
(Figure 10.68). mesodermal stem cells of the liver.
Based on their three-dimensional morphology, Kupffer
LIVER SINUSOID (VAS SINUSOIDEUM) cells are also referred to as stellate macrophages. They may
The blood capillaries of the liver have several special char- become partly detached from the endothelium or bulge
acteristics. They are extensively interconnected, up to 0.5 into the sinusoid. Kupffer cells phagocytose circulating
mm long and, depending on the functional status of the cell fragments, damaged blood cells, bacteria, immune
liver, 5–15 μm wide with irregular outpouchings. Increases complexes, fibrin and dissolved substances. They store and
in lumen diameter greatly slow the flow of blood, con- release iron. In contrast to endothelial cells, Kupffer cells
siderably facilitating exchange of substances with the contain abundant organelles, particularly phagosomes, lys-
hepatocyte. At least one surface of each hepatocyte faces osomes and peroxisomes. They are characterised by high
a sinusoid. Morphologically, sinusoids are characterised by peroxidase activity.
the following features: As cells of the MPS system, Kupffer cells also participate
in breakdown of haemoglobin originating from erythro-
· endothelial cells with pores, endothelial vesicles and cytes. This results in the formation of bilirubin, which is
intercellular openings, released by the Kupffer cells and passes into hepatocytes.
· discontinuous basal lamina and In the smooth ER of the hepatocyte, bilirubin (insoluble
· the presence of Kupffer cells. in water) is enzymatically converted into soluble bilirubin
glucuronide and transported through the bile ducts to the
WALL OF SINUSOID intestine, from whence it is excreted as urobilinogen.
Hepatic sinusoids are lined with flattened endothelial In addition, Kupffer cells synthesise PGD , PGE and
2 2
cells that frequently contain non-fenestrated micropi- other prostaglandins, interleukin-1 and -2, leukotriene D
4
nocytic vesicles (coated vesicles). Numerous irregularly and C as well as interferon and tumour necrosis factor.
4
spaced pores (diameter up to 0.5 μm) are usually present.
Intercellular spaces occur sporadically throughout the PERISINUSOIDAL SPACE (SPATIUM
endothelial lining. As the basal lamina is discontinuous, PERISINUSOIDEUM)
pores and intercellular spaces permit the free passage of Between the wall of the sinusoids and the surface of the
substances between the lumen of the sinusoid and the peri- hepatocytes is a narrow space (0.5–1 μm), the perisinu-
sinusoidal space of Dissé (see below). soidal space (space of Dissé; spatium perisinusoideum)
(Figure 10.78).
The perisinusoidal space plays an important part in reg-
ulating interactions between the sinusoid endothelium and
Vet Histology.indb 229 16/07/2019 15:02