Page 289 - Veterinary Histology of Domestic Mammals and Birds, 5th Edition
P. 289
Urinary system (organa urinaria) 271
VetBooks.ir
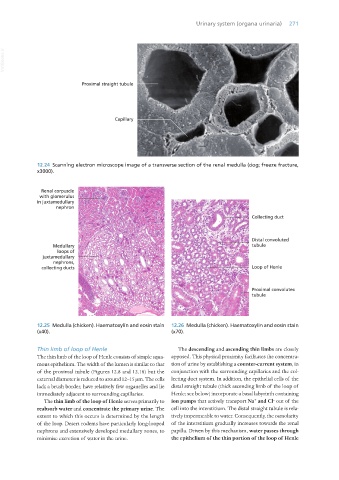
12.24 Scanning electron microscope image of a transverse section of the renal medulla (dog; freeze fracture,
x3000).
12.25 Medulla (chicken). Haematoxylin and eosin stain 12.26 Medulla (chicken). Haematoxylin and eosin stain
(x40). (x70).
Thin limb of loop of Henle The descending and ascending thin limbs are closely
The thin limb of the loop of Henle consists of simple squa- apposed. This physical proximity facilitates the concentra-
mous epithelium. The width of the lumen is similar to that tion of urine by establishing a counter-current system, in
of the proximal tubule (Figures 12.8 and 12.18) but the conjunction with the surrounding capillaries and the col-
external diameter is reduced to around 12–15 μm. The cells lecting duct system. In addition, the epithelial cells of the
lack a brush border, have relatively few organelles and lie distal straight tubule (thick ascending limb of the loop of
immediately adjacent to surrounding capillaries. Henle; see below) incorporate a basal labyrinth containing
+
The thin limb of the loop of Henle serves primarily to ion pumps that actively transport Na and Cl out of the
–
reabsorb water and concentrate the primary urine. The cell into the interstitium. The distal straight tubule is rela-
extent to which this occurs is determined by the length tively impermeable to water. Consequently, the osmolarity
of the loop. Desert rodents have particularly long-looped of the interstitium gradually increases towards the renal
nephrons and extensively developed medullary zones, to papilla. Driven by this mechanism, water passes through
minimise excretion of water in the urine. the epithelium of the thin portion of the loop of Henle
Vet Histology.indb 271 16/07/2019 15:04