Page 288 - Veterinary Histology of Domestic Mammals and Birds, 5th Edition
P. 288
270 Veterinary Histology of Domestic Mammals and Birds
VetBooks.ir
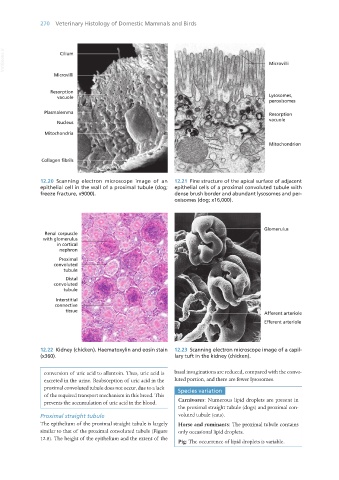
12.20 Scanning electron microscope image of an 12.21 Fine structure of the apical surface of adjacent
epithelial cell in the wall of a proximal tubule (dog; epithelial cells of a proximal convoluted tubule with
freeze fracture, x9000). dense brush border and abundant lysosomes and per-
oxisomes (dog; x16,000).
12.22 Kidney (chicken). Haematoxylin and eosin stain 12.23 Scanning electron microscope image of a capil-
(x360). lary tuft in the kidney (chicken).
conversion of uric acid to allantoin. Thus, uric acid is basal invaginations are reduced, compared with the convo-
excreted in the urine. Reabsorption of uric acid in the luted portion, and there are fewer lysosomes.
proximal convoluted tubule does not occur, due to a lack Species variation
of the required transport mechanism in this breed. This
prevents the accumulation of uric acid in the blood. Carnivores: Numerous lipid droplets are present in
the proximal straight tubule (dogs) and proximal con-
Proximal straight tubule voluted tubule (cats).
The epithelium of the proximal straight tubule is largely Horse and ruminants: The proximal tubule contains
similar to that of the proximal convoluted tubule (Figure only occasional lipid droplets.
12.8). The height of the epithelium and the extent of the
Pig: The occurrence of lipid droplets is variable.
Vet Histology.indb 270 16/07/2019 15:03