Page 287 - Veterinary Histology of Domestic Mammals and Birds, 5th Edition
P. 287
Urinary system (organa urinaria) 269
the apical cell surface there is a brush border (microvilli, up infoldings of the plasma membrane in which mitochondria
VetBooks.ir to 1 μm in length) that can be seen with the light micro- are localised. The basal labyrinth plays an important role
scope. The cytoplasm is acidophilic, and the cell borders in the reabsorption of electrolytes and water. Sodium
2+
+
are indistinct. Basally, prominent striations are formed by ions are transported by ion pumps (Mg -dependent Na -/
+
invaginations of the plasmalemma enclosing stacks of K -activated ATPase) into the expanded extracellular
elongated mitochondria. The brush border is coated by space. Energy is supplied by ATP produced by the abun-
a glycocalyx containing membrane enzymes (e.g. alka- dant local mitochondria. Chloride ions and water passively
+
line phosphatase, peptidases). The glycocalyx is visible by follow the actively transported Na . The removal of Na
+
electron microscopy. and Cl ions from the base of the cell maintains a gradient
–
At the base of the microvilli, the cytoplasm contains between the tubular lumen and the surrounding capillar-
+
numerous vesicles and tubular infoldings of the cell ies, driving absorption of Na from the glomerular filtrate.
membrane. In addition, the apical portion of the cell By the end of the proximal tubule, over two-thirds of the
contains large numbers of lysosomes, peroxisomes and water filtered by the glomerulus has been reabsorbed from
resorption vacuoles (Figures 12.20 and 12.21). These the tubular lumen. This passes through the epithelium into
organelles are required for the extensive trans-epithelial the peri-tubular capillary system. Trans-epithelial fluid trans-
uptake of substances from the tubular lumen. The absorp- port is facilitated by the oncotic pressure of the highly viscous
tive capacity of the cell is increased considerably by the blood in the postglomerular vessels. Other processes occur-
density of microvilli in the brush border (up to 7000 per ring in the wall of the proximal convoluted tubule include:
cell). The cells of the proximal tubule are responsible for:
· reabsorption of bicarbonate and glucose via mem-
· reabsorption of proteins and amino acids by pinocy- brane transport proteins and
tosis (transcellular pathway) and · gluconeogenesis in the peroxisomes, via energy sup-
· active transport of sodium into the intercellular plied by fatty acids.
space (paracellular pathway).
The epithelium of the proximal tubule also secretes
Proteins passing through the apical cell membrane are taken various substances. Products of metabolism and foreign
up and enzymatically degraded by lysosomes. Peptides are substances (e.g. drugs) are actively secreted. Electrolytes,
+
+
cleaved by membrane enzymes (e.g. aminopeptidases, NH ions and H ions pass passively from the cell into the
4
transferases) to form amino acids. Under normal condi- tubular lumen.
tions, the urine that is finally excreted is free of proteins. Species variation
At the base of the epithelium, extensive interdigitation
of branching processes of neighbouring cells gives rise to Dog: In the Dalmatian, the liver enzyme uricase appears
a basal labyrinth. In histological section, this appears as to be biologically unavailable, limiting the capacity for
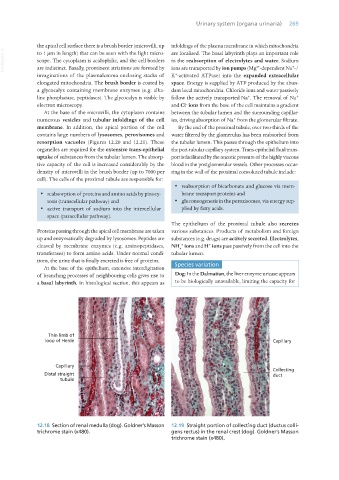
12.18 Section of renal medulla (dog). Goldner’s Masson 12.19 Straight portion of collecting duct (ductus colli-
trichrome stain (x480). gens rectus) in the renal crest (dog). Goldner’s Masson
trichrome stain (x480).
Vet Histology.indb 269 16/07/2019 15:03