Page 299 - Veterinary Histology of Domestic Mammals and Birds, 5th Edition
P. 299
Male reproductive system (organa genitalia masculina) 281
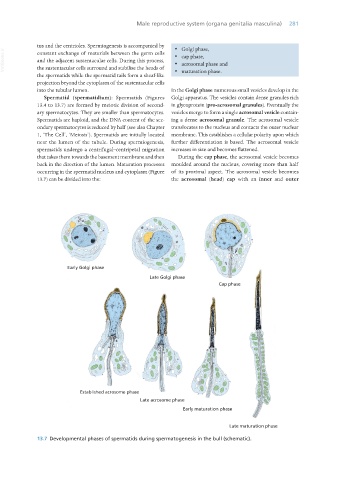
tus and the centrioles. Spermiogenesis is accompanied by · Golgi phase,
VetBooks.ir constant exchange of materials between the germ cells · cap phase,
and the adjacent sustentacular cells. During this process,
· acrosomal phase and
the sustentacular cells surround and stabilise the heads of
the spermatids while the spermatid tails form a sheaf-like · maturation phase.
projection beyond the cytoplasm of the sustentacular cells
into the tubular lumen. In the Golgi phase numerous small vesicles develop in the
Spermatid (spermatidium): Spermatids (Figures Golgi apparatus. The vesicles contain dense granules rich
13.4 to 13.7) are formed by meiotic division of second- in glycoprotein (pro-acrosomal granules). Eventually the
ary spermatocytes. They are smaller than spermatocytes. vesicles merge to form a single acrosomal vesicle contain-
Spermatids are haploid, and the DNA content of the sec- ing a dense acrosomal granule. The acrosomal vesicle
ondary spermatocytes is reduced by half (see also Chapter translocates to the nucleus and contacts the outer nuclear
1, ‘The Cell’, ‘Meiosis’). Spermatids are initially located membrane. This establishes a cellular polarity upon which
near the lumen of the tubule. During spermiogenesis, further differentiation is based. The acrosomal vesicle
spermatids undergo a centrifugal–centripetal migration increases in size and becomes flattened.
that takes them towards the basement membrane and then During the cap phase, the acrosomal vesicle becomes
back in the direction of the lumen. Maturation processes moulded around the nucleus, covering more than half
occurring in the spermatid nucleus and cytoplasm (Figure of its proximal aspect. The acrosomal vesicle becomes
13.7) can be divided into the: the acrosomal (head) cap with an inner and outer
13.7 Developmental phases of spermatids during spermatogenesis in the bull (schematic).
Vet Histology.indb 281 16/07/2019 15:04