Page 300 - Veterinary Histology of Domestic Mammals and Birds, 5th Edition
P. 300
282 Veterinary Histology of Domestic Mammals and Birds
acrosomal membrane. The space between the inner with the nuclear membrane. The acrosome covers two-
VetBooks.ir acrosomal membrane and the outer nuclear membrane is thirds of the nucleus and the manchette has receded. The
the subacrosomal space. Beneath the acrosomal cap, the annulus is displaced distally, accompanied by mitochon-
chromatin increases in density. The bulk of the cytoplasm, dria. The flagellum is fully formed. The mitochondria,
including the organelles, becomes displaced to the distal components of the future middle piece, are arranged heli-
aspect of the spermatid nucleus. The diplosome (centriole cally around the flagellum. Distal to the mitochondrial
pair) lies at the distal pole of the nucleus. The proximal covering, the axoneme is surrounded by outer fibres and
centriole is in contact with the nuclear membrane at the a fibrous sheath (future principal piece). Once the sperm
site of the implantation fossa. tail has differentiated, the cytoplasm is pinched off and the
During the acrosomal phase the nucleus gradu- resulting residual body is phagocytosed by sustentacular
ally becomes anterio-posteriorly elongated, flattened cells.
and condensed. The space between the inner and outer Spermatozoon: The spermatozoon (Figures 13.8 to
acrosomal membranes is filled completely with glycopro- 13.10) is the end-product of spermiogenesis. It is fully dif-
tein-rich material. The acrosomal cap becomes the definitive ferentiated in a morphological sense but is not yet capable
acrosome (see below). of fertilisation. Maturation continues during its passage
By this stage the spermatid has an elongated appear- through the epididymis.
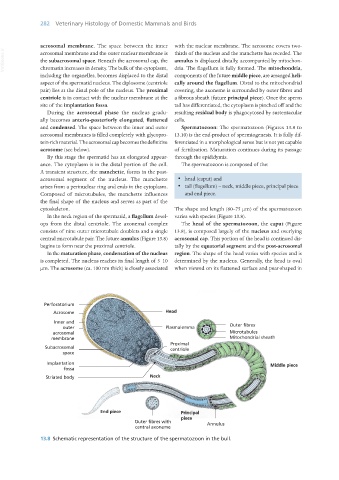
ance. The cytoplasm is in the distal portion of the cell. The spermatozoon is composed of the:
A transient structure, the manchette, forms in the post-
acrosomal segment of the nucleus. The manchette · head (caput) and
arises from a perinuclear ring and ends in the cytoplasm. · tail (flagellum) – neck, middle piece, principal piece
Composed of microtubules, the manchette influences and end piece.
the final shape of the nucleus and serves as part of the
cytoskeleton. The shape and length (60–75 μm) of the spermatozoon
In the neck region of the spermatid, a flagellum devel- varies with species (Figure 13.8).
ops from the distal centriole. The axonemal complex The head of the spermatozoon, the caput (Figure
consists of nine outer microtubule doublets and a single 13.8), is composed largely of the nucleus and overlying
central microtubule pair. The future annulus (Figure 13.8) acrosomal cap. This portion of the head is continued dis-
begins to form near the proximal centriole. tally by the equatorial segment and the post-acrosomal
In the maturation phase, condensation of the nucleus region. The shape of the head varies with species and is
is completed. The nucleus reaches its final length of 5–10 determined by the nucleus. Generally, the head is oval
μm. The acrosome (ca. 100 nm thick) is closely associated when viewed on its flattened surface and pear-shaped in
13.8 Schematic representation of the structure of the spermatozoon in the bull.
Vet Histology.indb 282 16/07/2019 15:04