Page 303 - Veterinary Histology of Domestic Mammals and Birds, 5th Edition
P. 303
Male reproductive system (organa genitalia masculina) 285
VetBooks.ir
Lipid
vacuole
Mitochondrion
Dense
cytoplasm of
sustentacular
cell
ER cisternae
Nucleus
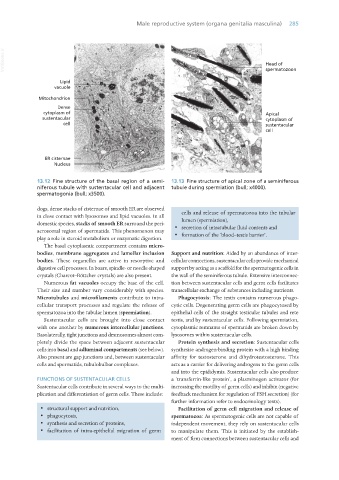
13.12 Fine structure of the basal region of a semi- 13.13 Fine structure of apical zone of a seminiferous
niferous tubule with sustentacular cell and adjacent tubule during spermiation (bull; x4000).
spermatogonia (bull; x3500).
dogs, dense stacks of cisternae of smooth ER are observed
in close contact with lysosomes and lipid vacuoles. In all cells and release of spermatozoa into the tubular
domestic species, stacks of smooth ER surround the peri- lumen (spermiation),
acrosomal region of spermatids. This phenomenon may · secretion of intratubular fluid contents and
play a role in steroid metabolism or enzymatic digestion. · formation of the ‘blood–testis barrier’.
The basal cytoplasmic compartment contains micro-
bodies, membrane aggregates and lamellar inclusion Support and nutrition: Aided by an abundance of inter-
bodies. These organelles are active in resorptive and cellular connections, sustentacular cells provide mechanical
digestive cell processes. In boars, spindle- or needle-shaped support by acting as a scaffold for the spermatogenic cells in
crystals (Charcot–Böttcher crystals) are also present. the wall of the seminiferous tubule. Extensive interconnec-
Numerous fat vacuoles occupy the base of the cell. tion between sustentacular cells and germ cells facilitates
Their size and number vary considerably with species. transcellular exchange of substances including nutrients.
Microtubules and microfilaments contribute to intra- Phagocytosis: The testis contains numerous phago-
cellular transport processes and regulate the release of cytic cells. Degenerating germ cells are phagocytosed by
spermatozoa into the tubular lumen (spermiation). epithelial cells of the straight testicular tubules and rete
Sustentacular cells are brought into close contact testis, and by sustentacular cells. Following spermiation,
with one another by numerous intercellular junctions. cytoplasmic remnants of spermatids are broken down by
Basolaterally, tight junctions and desmosomes almost com- lysosomes within sustentacular cells.
pletely divide the space between adjacent sustentacular Protein synthesis and secretion: Sustentacular cells
cells into basal and adluminal compartments (see below). synthesise androgen-binding protein with a high binding
Also present are gap junctions and, between sustentacular affinity for testosterone and dihydrotestosterone. This
cells and spermatids, tubulobulbar complexes. acts as a carrier for delivering androgens to the germ cells
and into the epididymis. Sustentacular cells also produce
FUNCTIONS OF SUSTENTACULAR CELLS a ‘transferrin-like protein’, a plasminogen activator (for
Sustentacular cells contribute in several ways to the multi- increasing the motility of germ cells) and inhibin (negative
plication and differentiation of germ cells. These include: feedback mechanism for regulation of FSH secretion) (for
further information refer to endocrinology texts).
· structural support and nutrition, Facilitation of germ cell migration and release of
· phagocytosis, spermatozoa: As spermatogenic cells are not capable of
· synthesis and secretion of proteins, independent movement, they rely on sustentacular cells
· facilitation of intra-epithelial migration of germ to manipulate them. This is initiated by the establish-
ment of firm connections between sustentacular cells and
Vet Histology.indb 285 16/07/2019 15:04