Page 306 - Veterinary Histology of Domestic Mammals and Birds, 5th Edition
P. 306
288 Veterinary Histology of Domestic Mammals and Birds
VetBooks.ir
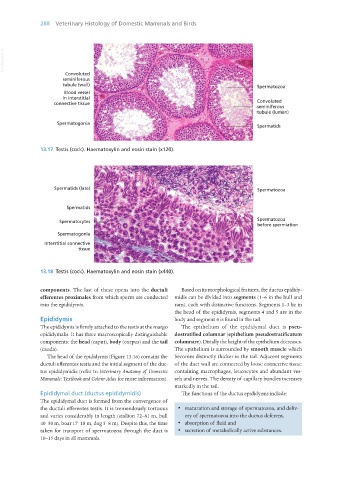
13.17 Testis (cock). Haematoxylin and eosin stain (x120).
13.18 Testis (cock). Haematoxylin and eosin stain (x440).
components. The last of these opens into the ductuli Based on its morphological features, the ductus epididy-
efferentes proximales from which sperm are conducted midis can be divided into segments (1–6 in the bull and
into the epididymis. ram), each with distinctive functions. Segments 1–3 lie in
the head of the epididymis, segments 4 and 5 are in the
Epididymis body and segment 6 is found in the tail.
The epididymis is firmly attached to the testis at the margo The epithelium of the epididymal duct is pseu-
epididymalis. It has three macroscopically distinguishable dostratified columnar (epithelium pseudostratificatum
components: the head (caput), body (corpus) and the tail columnare). Distally the height of the epithelium decreases.
(cauda). The epithelium is surrounded by smooth muscle which
The head of the epididymis (Figure 13.16) contains the becomes distinctly thicker in the tail. Adjacent segments
ductuli efferentes testis and the initial segment of the duc- of the duct wall are connected by loose connective tissue
tus epididymidis (refer to Veterinary Anatomy of Domestic containing macrophages, leucocytes and abundant ves-
Mammals: Textbook and Colour Atlas for more information). sels and nerves. The density of capillary bundles increases
markedly in the tail.
Epididymal duct (ductus epididymidis) The functions of the ductus epididymis include:
The epididymal duct is formed from the convergence of
the ductuli efferentes testis. It is tremendously tortuous · maturation and storage of spermatozoa, and deliv-
and varies considerably in length (stallion 72–81 m, bull ery of spermatozoa into the ductus deferens,
40–50 m, boar 17–18 m, dog 5–8 m). Despite this, the time · absorption of fluid and
taken for transport of spermatozoa through the duct is · secretion of metabolically active substances.
10–15 days in all mammals.
Vet Histology.indb 288 16/07/2019 15:04