Page 311 - Veterinary Histology of Domestic Mammals and Birds, 5th Edition
P. 311
Male reproductive system (organa genitalia masculina) 293
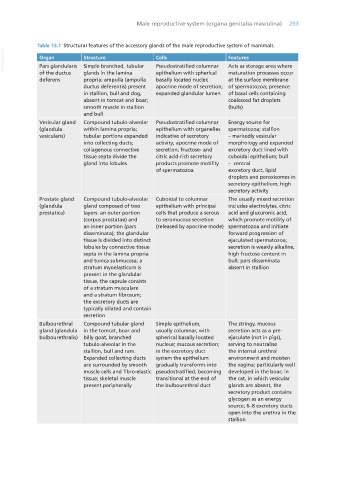
Table 13.1 Structural features of the accessory glands of the male reproductive system of mammals.
VetBooks.ir Organ Structure Cells Features
Acts as storage area where
Simple branched, tubular
Pseudostratified columnar
Pars glandularis
of the ductus glands in the lamina epithelium with spherical maturation processes occur
deferens propria; ampulla (ampulla basally located nuclei; at the surface membrane
ductus deferentis) present apocrine mode of secretion; of spermatozoa; presence
in stallion, bull and dog, expanded glandular lumen of basal cells containing
absent in tomcat and boar; coalesced fat droplets
smooth muscle in stallion (bulls)
and bull
Vesicular gland Compound tubulo-alveolar Pseudostratified columnar Energy source for
(glandula within lamina propria; epithelium with organelles spermatozoa; stallion
vesicularis) tubular portions expanded indicative of secretory – markedly vesicular
into collecting ducts; activity; apocrine mode of morphology and expanded
collagenous connective secretion; fructose- and excretory duct lined with
tissue septa divide the citric acid-rich secretory cuboidal epithelium; bull
gland into lobules products promote motility – central
of spermatozoa excretory duct, lipid
droplets and peroxisomes in
secretory epithelium; high
secretory activity
Prostate gland Compound tubulo-alveolar Cuboidal to columnar The usually mixed secretion
(glandula gland composed of two epithelium with principal includes electrolytes, citric
prostatica) layers: an outer portion cells that produce a serous acid and glucuronic acid,
(corpus prostatae) and to seromucous secretion which promote motility of
an inner portion (pars (released by apocrine mode) spermatozoa and initiate
disseminata); the glandular forward progression of
tissue is divided into distinct ejaculated spermatozoa;
lobules by connective tissue secretion is weakly alkaline,
septa in the lamina propria high fructose content in
and tunica submucosa; a bull; pars disseminata
stratum myoelasticum is absent in stallion
present in the glandular
tissue, the capsule consists
of a stratum musculare
and a stratum fibrosum;
the excretory ducts are
typically dilated and contain
secretion
Bulbourethral Compound tubular gland Simple epithelium, The stringy, mucous
gland (glandula in the tomcat, boar and usually columnar, with secretion acts as a pre-
bulbourethralis) billy goat, branched spherical basally located ejaculate (not in pigs),
tubulo-alveolar in the nucleus; mucous secretion; serving to neutralise
stallion, bull and ram. in the excretory duct the internal urethral
Expanded collecting ducts system the epithelium environment and moisten
are surrounded by smooth gradually transforms into the vagina; particularly well
muscle cells and fibro-elastic pseudostratified, becoming developed in the boar; in
tissue; skeletal muscle transitional at the end of the cat, in which vesicular
present peripherally the bulbourethral duct glands are absent, the
secretory product contains
glycogen as an energy
source; 6–8 excretory ducts
open into the urethra in the
stallion
Vet Histology.indb 293 16/07/2019 15:05