Page 312 - Veterinary Histology of Domestic Mammals and Birds, 5th Edition
P. 312
294 Veterinary Histology of Domestic Mammals and Birds
VetBooks.ir
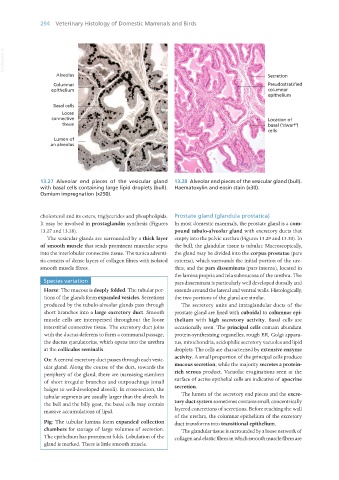
Alveolus
Columnar
epithelium
Basal cells
Loose
connective
tissue
Lumen of
an alveolus
13.27 Alveolar end pieces of the vesicular gland 13.28 Alveolar end pieces of the vesicular gland (bull).
with basal cells containing large lipid droplets (bull). Haematoxylin and eosin stain (x30).
Osmium impregnation (x250).
cholesterol and its esters, triglycerides and phospholipids. Prostate gland (glandula prostatica)
It may be involved in prostaglandin synthesis (Figures In most domestic mammals, the prostate gland is a com-
13.27 and 13.28). pound tubulo-alveolar gland with excretory ducts that
The vesicular glands are surrounded by a thick layer empty into the pelvic urethra (Figures 13.29 and 13.30). In
of smooth muscle that sends prominent muscular septa the bull, the glandular tissue is tubular. Macroscopically,
into the interlobular connective tissue. The tunica adventi- the gland may be divided into the corpus prostatae (pars
tia consists of dense layers of collagen fibres with isolated externa), which surrounds the initial portion of the ure-
smooth muscle fibres. thra, and the pars disseminata (pars interna), located in
the lamina propria and tela submucosa of the urethra. The
Species variation pars disseminata is particularly well developed dorsally and
Horse: The mucosa is deeply folded. The tubular por- extends around the lateral and ventral walls. Histologically,
tions of the glands form expanded vesicles. Secretions the two portions of the gland are similar.
produced by the tubulo-alveolar glands pass through The secretory units and intraglandular ducts of the
short branches into a large excretory duct. Smooth prostate gland are lined with cuboidal to columnar epi-
muscle cells are interspersed throughout the loose thelium with high secretory activity. Basal cells are
interstitial connective tissue. The excretory duct joins occasionally seen. The principal cells contain abundant
with the ductus deferens to form a communal passage, protein-synthesising organelles, rough ER, Golgi appara-
the ductus ejaculatorius, which opens into the urethra tus, mitochondria, acidophilic secretory vacuoles and lipid
at the colliculus seminalis. droplets. The cells are characterised by extensive enzyme
Ox: A central excretory duct passes through each vesic- activity. A small proportion of the principal cells produce
ular gland. Along the course of the duct, towards the mucous secretion, while the majority secretes a protein-
periphery of the gland, there are increasing numbers rich serous product. Vacuolar evaginations seen at the
of short irregular branches and outpouchings (small surface of active epithelial cells are indicative of apocrine
bulges to well-developed alveoli). In cross-section, the secretion.
tubular segments are usually larger than the alveoli. In The lumen of the secretory end pieces and the excre-
the bull and the billy goat, the basal cells may contain tory duct system sometimes contains small, concentrically
massive accumulations of lipid. layered concretions of secretions. Before reaching the wall
of the urethra, the columnar epithelium of the excretory
Pig: The tubular lumina form expanded collection duct transforms into transitional epithelium.
chambers for storage of large volumes of secretion. The glandular tissue is surrounded by a loose network of
The epithelium has prominent folds. Lobulation of the collagen and elastic fibres in which smooth muscle fibres are
gland is marked. There is little smooth muscle.
Vet Histology.indb 294 16/07/2019 15:05