Page 37 - Equine Clinical Medicine, Surgery and Reproduction, 2nd Edition
P. 37
12 CHAPTER 1
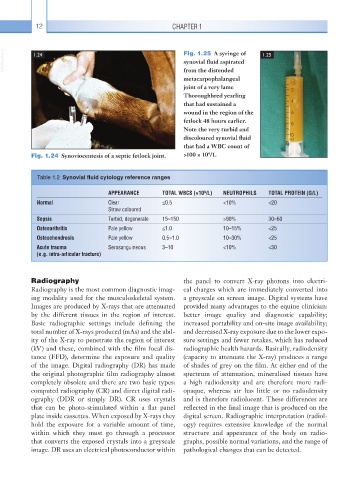
VetBooks.ir 1.24 Fig. 1.25 A syringe of 1.25
synovial fluid aspirated
from the distended
metacarpophalangeal
joint of a very lame
Thoroughbred yearling
that had sustained a
wound in the region of the
fetlock 48 hours earlier.
Note the very turbid and
discoloured synovial fluid
that had a WBC count of
9
Fig. 1.24 Synoviocentesis of a septic fetlock joint. >100 × 10 /1.
Table 1.2 Synovial fluid cytology reference ranges
9
APPEARANCE TOTAL WBCS (×10 /L) NEUTROPHILS TOTAL PROTEIN (G/L)
Normal Clear ≤0.5 <10% <20
Straw coloured
Sepsis Turbid, degenerate 15–150 >90% 30–60
Osteoarthritis Pale yellow ≤1.0 10–15% <25
Osteochondrosis Pale yellow 0.5–1.0 10–30% <25
Acute trauma Serosanguineous 3–10 <10% <30
(e.g. intra-articular fracture)
Radiography the panel to convert X-ray photons into electri-
Radiography is the most common diagnostic imag- cal charges which are immediately converted into
ing modality used for the musculoskeletal system. a greyscale on screen image. Digital systems have
Images are produced by X-rays that are attenuated provided many advantages to the equine clinician:
by the different tissues in the region of interest. better image quality and diagnostic capability;
Basic radiographic settings include defining the increased portability and on-site image availability;
total number of X-rays produced (mAs) and the abil- and decreased X-ray exposure due to the lower expo-
ity of the X-ray to penetrate the region of interest sure settings and fewer retakes, which has reduced
(kV) and these, combined with the film focal dis- radiographic health hazards. Basically, radiodensity
tance (FFD), determine the exposure and quality (capacity to attenuate the X-ray) produces a range
of the image. Digital radiography (DR) has made of shades of grey on the film. At either end of the
the original photographic film radiography almost spectrum of attenuation, mineralised tissues have
completely obsolete and there are two basic types: a high radiodensity and are therefore more radi-
computed radiography (CR) and direct digital radi- opaque, whereas air has little or no radiodensity
ography (DDR or simply DR). CR uses crystals and is therefore radiolucent. These differences are
that can be photo-stimulated within a flat panel reflected in the final image that is produced on the
plate inside cassettes. When exposed by X-rays they digital screen. Radiographic interpretation (radiol-
hold the exposure for a variable amount of time, ogy) requires extensive knowledge of the normal
within which they must go through a processor structure and appearance of the body on radio-
that converts the exposed crystals into a greyscale graphs, possible normal variations, and the range of
image. DR uses an electrical photoconductor within pathological changes that can be detected.