Page 246 - Manual of Equine Field Surgery
P. 246
242 FEMALE UROGENITAL SURGERIES
A
A
~ : , : ::::.::)
·--
8 8
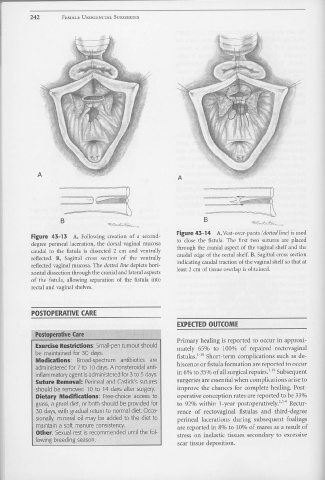
Figure 43-14 A, Vest-over-pants (dotted line) is used
Figure 43-13 A, Following creation of a second-
degree perinea! laceration, the dorsal vaginal mucosa to close the fistula. The first two sutures are placed
caudal to the fistula is dissected 2 cm and ventrally through the cranial aspect of the vaginal shelf and the
reflected. B, Sagittal cross section of the ventrally caudal edge of the rectal shelf. B, Sagittal cross section
reflected vaginal mucosa. The dotted line depicts hori- indicating caudal traction of the vaginal shelf so that at
zontal dissection through the cranial and lateral aspects least 2 cm of tissue overlap is obtained.
of the fistula, allowing separation of the fistula into
rectal and vaginal shelves.
POSTOPERATIVE CARE
EXPECTED OUTCOME
Postoperative Care
Primary healing is reported to occur in approxi-
Exercise Restridions: Small-pen turnout should mately 65°/o to 1000/o of repaired rectovaginal
be maintained for 30 days. fistulas.l" Short-term complications such as de-
Medications: Broad-spectrum antibiotics are
administered for 7 to 1 O days. A nonsteroidal anti- hiscence or fistula formation are reported to occur
inflammatory agent is administered for 3 to 5 days. in 6o/o to 35o/o of all surgical repairs.l"" Subsequent
Suture Removal: Perinea] and Caslick's sutures surgeries are essential when complications arise to
should be removed l O to 14 days after surgery. improve the chances for complete healing. Post-
Dietary Modifications: Free-choice access to operative conception rates are reported to be 330/0
grass, a gruel diet, or both should be provided for to 92°/o within 1-year postoperatively.v'" Recur-
30 days, with gradual return to normal diet. Occa- rence of rectovaginal fistulas and third-degree
sionally, mineral oil may be added to the diet to perineal lacerations during subsequent foalings
maintain a soft manure consistency. are reported in 8°/o to 10% of mares as a result of
Other: Sexual rest is recommended until the fol- stress on inelastic tissues secondary to excessive
lowing breeding season.
scar tissue deposition.