Page 660 - Clinical Small Animal Internal Medicine
P. 660
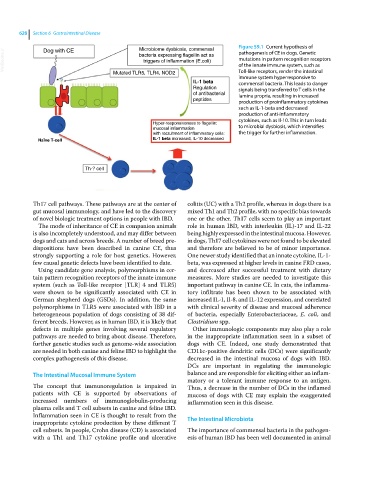
628 Section 6 Gastrointestinal Disease Figure 59.1 Current hypothesis of
VetBooks.ir Dog with CE Microbiome dysbiosis, commensal pathogenesis of CE in dogs. Genetic
bacteria expressing flagellin act as
mutations in pattern recognition receptors
triggers of inflammation (E.coli)
of the innate immune system, such as
Mutated TLR5, TLR4, NOD2 Toll‐like receptors, render the intestinal
immune system hyperresponsive to
IL-1 beta commensal bacteria. This leads to danger
Regulation signals being transferred to T cells in the
of antibacterial lamina propria, resulting in increased
peptides production of proinflammatory cytokines
such as IL‐1‐beta and decreased
production of anti-inflammatory
cytokines, such as Il‐10. This in turn leads
Hyper-responsiveness to flagellin:
mucosal inflammation to microbial dysbiosis, which intensifies
with recruitment of inflammatory cells: the trigger for further inflammation.
Naïve T-cell IL-1 beta increased, IL-10 decreased
Th-? cell
Th17 cell pathways. These pathways are at the center of colitis (UC) with a Th2 profile, whereas in dogs there is a
gut mucosal immunology, and have led to the discovery mixed Th1 and Th2 profile, with no specific bias towards
of novel biologic treatment options in people with IBD. one or the other. Th17 cells seem to play an important
The mode of inheritance of CE in companion animals role in human IBD, with interleukin (IL)‐17 and IL‐22
is also incompletely understood, and may differ between being highly expressed in the intestinal mucosa. However,
dogs and cats and across breeds. A number of breed pre- in dogs, Th17 cell cytokines were not found to be elevated
dispositions have been described in canine CE, thus and therefore are believed to be of minor importance.
strongly supporting a role for host genetics. However, One newer study identified that an innate cytokine, IL‐1‐
few causal genetic defects have been identified to date. beta, was expressed at higher levels in canine FRD cases,
Using candidate gene analysis, polymorphisms in cer- and decreased after successful treatment with dietary
tain pattern recognition receptors of the innate immune measures. More studies are needed to investigate this
system (such as Toll‐like receptor [TLR] 4 and TLR5) important pathway in canine CE. In cats, the inflamma-
were shown to be significantly associated with CE in tory infiltrate has been shown to be associated with
German shepherd dogs (GSDs). In addition, the same increased IL‐1, Il‐8, and IL‐12 expression, and correlated
polymorphisms in TLR5 were associated with IBD in a with clinical severity of disease and mucosal adherence
heterogeneous population of dogs consisting of 38 dif- of bacteria, especially Enterobacteriaceae, E. coli, and
ferent breeds. However, as in human IBD, it is likely that Clostridium spp.
defects in multiple genes involving several regulatory Other immunologic components may also play a role
pathways are needed to bring about disease. Therefore, in the inappropriate inflammation seen in a subset of
further genetic studies such as genome‐wide association dogs with CE. Indeed, one study demonstrated that
are needed in both canine and feline IBD to highlight the CD11c‐positive dendritic cells (DCs) were significantly
complex pathogenesis of this disease. decreased in the intestinal mucosa of dogs with IBD.
DCs are important in regulating the immunologic
The Intestinal Mucosal Immune System balance and are responsible for eliciting either an inflam-
matory or a tolerant immune response to an antigen.
The concept that immunoregulation is impaired in Thus, a decrease in the number of DCs in the inflamed
patients with CE is supported by observations of mucosa of dogs with CE may explain the exaggerated
increased numbers of immunoglobulin‐producing inflammation seen in this disease.
plasma cells and T cell subsets in canine and feline IBD.
Inflammation seen in CE is thought to result from the The Intestinal Microbiota
inappropriate cytokine production by these different T
cell subsets. In people, Crohn disease (CD) is associated The importance of commensal bacteria in the pathogen-
with a Th1 and Th17 cytokine profile and ulcerative esis of human IBD has been well documented in animal