Page 549 - Veterinary Immunology, 10th Edition
P. 549
VetBooks.ir Endogenous Antigens
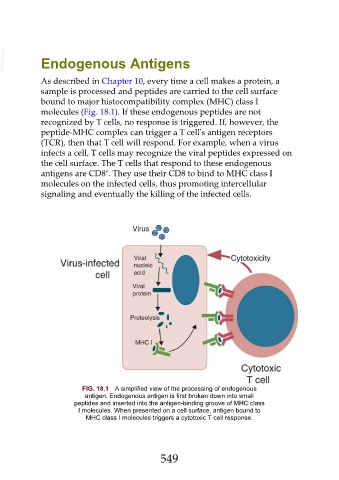
As described in Chapter 10, every time a cell makes a protein, a
sample is processed and peptides are carried to the cell surface
bound to major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I
molecules (Fig. 18.1). If these endogenous peptides are not
recognized by T cells, no response is triggered. If, however, the
peptide-MHC complex can trigger a T cell's antigen receptors
(TCR), then that T cell will respond. For example, when a virus
infects a cell, T cells may recognize the viral peptides expressed on
the cell surface. The T cells that respond to these endogenous
+
antigens are CD8 . They use their CD8 to bind to MHC class I
molecules on the infected cells, thus promoting intercellular
signaling and eventually the killing of the infected cells.
FIG. 18.1 A simplified view of the processing of endogenous
antigen. Endogenous antigen is first broken down into small
peptides and inserted into the antigen-binding groove of MHC class
I molecules. When presented on a cell surface, antigen bound to
MHC class I molecules triggers a cytotoxic T cell response.
549