Page 586 - Veterinary Immunology, 10th Edition
P. 586
VetBooks.ir Innate Cytotoxic Cells
Natural Killer Cells
The first ILCs identified were called natural killer (NK) cells
because they were able to kill virus-infected and tumor cells
without requiring prior activation. NK cells can be considered to be
cytotoxic ILC1s. In most mammals, NK cells are large, granular
lymphocytes. In cattle, NK cells are large cells, but may not contain
large cytoplasmic granules (Fig. 19.5). There is debate about NK cell
morphology in the pig. Some investigators claim that they are large
granular lymphocytes, whereas others believe that they are small
lymphocytes without obvious cytoplasmic granules.
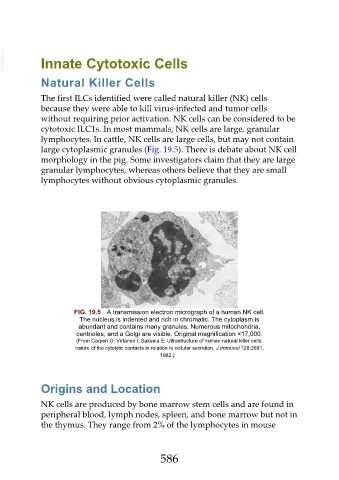
FIG. 19.5 A transmission electron micrograph of a human NK cell.
The nucleus is indented and rich in chromatic. The cytoplasm is
abundant and contains many granules. Numerous mitochondria,
centrioles, and a Golgi are visible. Original magnification ×17,000.
(From Carpen O, Virtanen I, Saksela E: Ultrastructure of human natural killer cells:
nature of the cytolytic contacts in relation to cellular secretion, J Immunol 128:2691,
1982.)
Origins and Location
NK cells are produced by bone marrow stem cells and are found in
peripheral blood, lymph nodes, spleen, and bone marrow but not in
the thymus. They range from 2% of the lymphocytes in mouse
586