Page 602 - Veterinary Immunology, 10th Edition
P. 602
VetBooks.ir
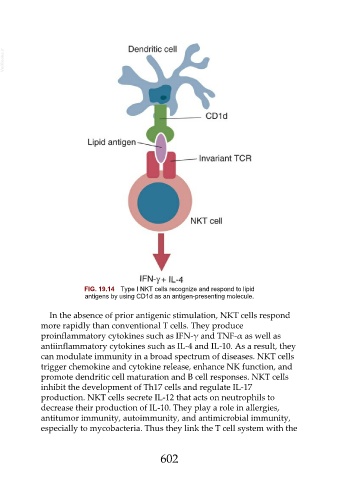
FIG. 19.14 Type I NKT cells recognize and respond to lipid
antigens by using CD1d as an antigen-presenting molecule.
In the absence of prior antigenic stimulation, NKT cells respond
more rapidly than conventional T cells. They produce
proinflammatory cytokines such as IFN-γ and TNF-α as well as
antiinflammatory cytokines such as IL-4 and IL-10. As a result, they
can modulate immunity in a broad spectrum of diseases. NKT cells
trigger chemokine and cytokine release, enhance NK function, and
promote dendritic cell maturation and B cell responses. NKT cells
inhibit the development of Th17 cells and regulate IL-17
production. NKT cells secrete IL-12 that acts on neutrophils to
decrease their production of IL-10. They play a role in allergies,
antitumor immunity, autoimmunity, and antimicrobial immunity,
especially to mycobacteria. Thus they link the T cell system with the
602