Page 112 - Veterinary Histology of Domestic Mammals and Birds, 5th Edition
P. 112
94 Veterinary Histology of Domestic Mammals and Birds
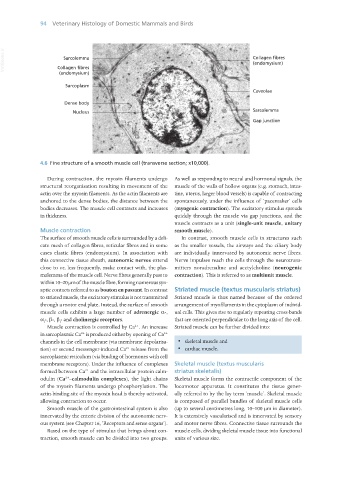
VetBooks.ir Sarcolemma Collagen fibres
(endomysium)
Collagen fibres
(endomysium)
Sarcoplasm
Caveolae
Dense body
Nucleus Sarcolemma
Gap junction
4.6 Fine structure of a smooth muscle cell (transverse section; x10,000).
During contraction, the myosin filaments undergo As well as responding to neural and hormonal signals, the
structural reorganisation resulting in movement of the muscle of the walls of hollow organs (e.g. stomach, intes-
actin over the myosin filaments. As the actin filaments are tine, uterus, larger blood vessels) is capable of contracting
anchored to the dense bodies, the distance between the spontaneously, under the influence of ‘pacemaker’ cells
bodies decreases. The muscle cell contracts and increases (myogenic contraction). The excitatory stimulus spreads
in thickness. quickly through the muscle via gap junctions, and the
muscle contracts as a unit (single-unit muscle, unitary
Muscle contraction smooth muscle).
The surface of smooth muscle cells is surrounded by a deli- In contrast, smooth muscle cells in structures such
cate mesh of collagen fibres, reticular fibres and in some as the smaller vessels, the airways and the ciliary body
cases elastic fibres (endomysium). In association with are individually innervated by autonomic nerve fibres.
this connective tissue sheath, autonomic nerves extend Nerve impulses reach the cells through the neurotrans-
close to or, less frequently, make contact with, the plas- mitters noradrenaline and acetylcholine (neurogenic
malemma of the muscle cell. Nerve fibres generally pass to contraction). This is referred to as multiunit muscle.
within 10–20 μm of the muscle fibre, forming numerous syn-
aptic contacts referred to as bouton en passant. In contrast Striated muscle (textus muscularis striatus)
to striated muscle, the excitatory stimulus is not transmitted Striated muscle is thus named because of the ordered
through a motor end plate. Instead, the surface of smooth arrangement of myofilaments in the cytoplasm of individ-
muscle cells exhibits a large number of adrenergic α-, ual cells. This gives rise to regularly repeating cross-bands
α-, β-, β- and cholinergic receptors. that are oriented perpendicular to the long axis of the cell.
l l
Muscle contraction is controlled by Ca . An increase Striated muscle can be further divided into:
2+
2+
2+
in sarcoplasmic Ca is produced either by opening of Ca
channels in the cell membrane (via membrane depolarisa- · skeletal muscle and
2+
tion) or second messenger-induced Ca release from the · cardiac muscle.
sarcoplasmic reticulum (via binding of hormones with cell
membrane receptors). Under the influence of complexes Skeletal muscle (textus muscularis
2+
formed between Ca and the intracellular protein calm- striatus skeletalis)
odulin (Ca –calmodulin complexes), the light chains Skeletal muscle forms the contractile component of the
2+
of the myosin filaments undergo phosphorylation. The locomotor apparatus. It constitutes the tissue gener-
actin-binding site of the myosin head is thereby activated, ally referred to by the lay term ‘muscle’. Skeletal muscle
allowing contraction to occur. is composed of parallel bundles of skeletal muscle cells
Smooth muscle of the gastrointestinal system is also (up to several centimetres long, 10–100 μm in diameter).
innervated by the enteric division of the autonomic nerv- It is extensively vascularised and is innervated by sensory
ous system (see Chapter 16, ‘Receptors and sense organs’). and motor nerve fibres. Connective tissue surrounds the
Based on the type of stimulus that brings about con- muscle cells, dividing skeletal muscle tissue into functional
traction, smooth muscle can be divided into two groups. units of various size.
Vet Histology.indb 94 16/07/2019 14:56