Page 113 - Veterinary Histology of Domestic Mammals and Birds, 5th Edition
P. 113
Muscle tissue (textus muscularis) 95
Fine structure of skeletal muscle cells dant in the mitochondria of muscle cells. They include
VetBooks.ir (myocytus striatus skeletalis) enzymes of the citric acid cycle and those associated with
The striated muscle cell is a syncytium formed by the β-oxidation (in the mitochondrial matrix), cytochrome oxi-
fusion of myogenic stem cells (myoblasts). An individual dase (inner mitochondrial membrane), adenylate kinase
cell, also referred to as a muscle fibre, contains over 100 for synthesis of energy-rich phosphates (intermembrane
nuclei (Table 4.1). The nuclei are flattened and fusiform space) and monoamine oxidase (outer membrane). The
and are predominantly located peripherally, at the inner cells contain relatively little rough ER and few free ribo-
surface of the plasmalemma (subplasmalemmal). somes. The sarcoplasm contains glycoprotein as a source of
Individual skeletal muscle cells are surrounded by energy, and the muscle pigment myoglobin for storage of
a basal lamina and a meshwork of reticular fibres. This O . Interspersed between the myofilaments are two struc-
2
casing lies immediately adjacent to the plasmalemma turally independent yet functionally coupled membrane
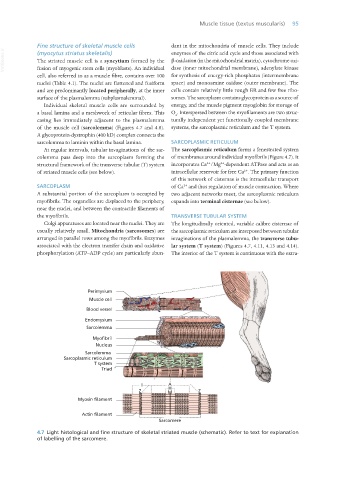
of the muscle cell (sarcolemma) (Figures 4.7 and 4.8). systems, the sarcoplasmic reticulum and the T system.
A glycoprotein-dystrophin (400 kD) complex connects the
sarcolemma to laminin within the basal lamina. SARCOPLASMIC RETICULUM
At regular intervals, tubular invaginations of the sar- The sarcoplasmic reticulum forms a fenestrated system
colemma pass deep into the sarcoplasm forming the of membranes around individual myofibrils (Figure 4.7). It
2+
2+
structural framework of the transverse tubular (T) system incorporates Ca /Mg -dependent ATPase and acts as an
2+
of striated muscle cells (see below). intracellular reservoir for free Ca . The primary function
of this network of cisternae is the intracellular transport
SARCOPLASM of Ca and thus regulation of muscle contraction. Where
2+
A substantial portion of the sarcoplasm is occupied by two adjacent networks meet, the sarcoplasmic reticulum
myofibrils. The organelles are displaced to the periphery, expands into terminal cisternae (see below).
near the nuclei, and between the contractile filaments of
the myofibrils. TRANSVERSE TUBULAR SYSTEM
Golgi apparatuses are located near the nuclei. They are The longitudinally oriented, variable calibre cisternae of
usually relatively small. Mitochondria (sarcosomes) are the sarcoplasmic reticulum are interposed between tubular
arranged in parallel rows among the myofibrils. Enzymes invaginations of the plasmalemma, the transverse tubu-
associated with the electron transfer chain and oxidative lar system (T system) (Figures 4.7, 4.11, 4.13 and 4.14).
phosphorylation (ATP–ADP cycle) are particularly abun- The interior of the T system is continuous with the extra-
Perimysium
Muscle cell
Blood vessel
Endomysium
Sarcolemma
Myofibril
Nucleus
Sarcolemma
Sarcoplasmic reticulum
T system
Triad
I A
H
Z M Z
Myosin filament
Actin filament
Sarcomere
4.7 Light histological and fine structure of skeletal striated muscle (schematic). Refer to text for explanation
of labelling of the sarcomere.
Vet Histology.indb 95 16/07/2019 14:56