Page 153 - Veterinary Histology of Domestic Mammals and Birds, 5th Edition
P. 153
Blood and haemopoiesis (sanguis et haemocytopoesis) 135
VetBooks.ir
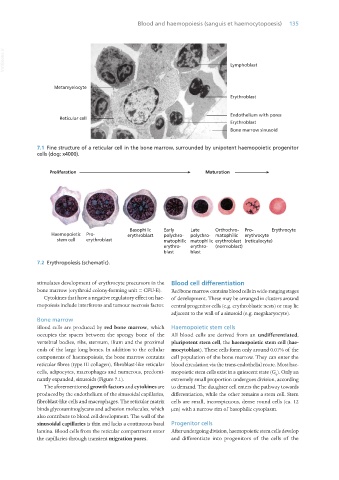
7.1 Fine structure of a reticular cell in the bone marrow, surrounded by unipotent haemopoietic progenitor
cells (dog; x4000).
7.2 Erythropoiesis (schematic).
stimulates development of erythrocyte precursors in the Blood cell differentiation
bone marrow (erythroid colony-forming unit = CFU-E). Red bone marrow contains blood cells in wide-ranging stages
Cytokines that have a negative regulatory effect on hae- of development. These may be arranged in clusters around
mopoiesis include interferons and tumour necrosis factor. central progenitor cells (e.g. erythroblastic nests) or may lie
adjacent to the wall of a sinusoid (e.g. megakaryocyte).
Bone marrow
Blood cells are produced by red bone marrow, which Haemopoietic stem cells
occupies the spaces between the spongy bone of the All blood cells are derived from an undifferentiated,
vertebral bodies, ribs, sternum, ilium and the proximal pluripotent stem cell, the haemopoietic stem cell (hae-
ends of the large long bones. In addition to the cellular mocytoblast). These cells form only around 0.01% of the
components of haemopoiesis, the bone marrow contains cell population of the bone marrow. They can enter the
reticular fibres (type III collagen), fibroblast-like reticular blood circulation via the trans-endothelial route. Most hae-
cells, adipocytes, macrophages and numerous, predomi- mopoietic stem cells exist in a quiescent state (G ). Only an
0
nantly expanded, sinusoids (Figure 7.1). extremely small proportion undergoes division, according
The aforementioned growth factors and cytokines are to demand. The daughter cell enters the pathway towards
produced by the endothelium of the sinusoidal capillaries, differentiation, while the other remains a stem cell. Stem
fibroblast-like cells and macrophages. The reticular matrix cells are small, inconspicuous, dense round cells (ca. 12
binds glycosaminoglycans and adhesion molecules, which μm) with a narrow rim of basophilic cytoplasm.
also contribute to blood cell development. The wall of the
sinusoidal capillaries is thin and lacks a continuous basal Progenitor cells
lamina. Blood cells from the reticular compartment enter After undergoing division, haemopoietic stem cells develop
the capillaries through transient migration pores. and differentiate into progenitors of the cells of the
Vet Histology.indb 135 16/07/2019 14:58