Page 234 - Veterinary Histology of Domestic Mammals and Birds, 5th Edition
P. 234
216 Veterinary Histology of Domestic Mammals and Birds
tions of the lamina propria lined with simple epithelium
VetBooks.ir (epithelium mucosae) (Figures 10.48 to 10.50).
Intestinal villi (length 0.5–1.5 mm, density 20–40/
2
mm ) contribute significantly to the total mucosal surface
area. In carnivores the villi are long and slender, while
those of ruminants are short and wide. In all domestic
mammals, the villi are longest in the jejunum, and shorter
in the duodenum and ileum (Figures 10.48 to 10.51).
MUCOSAL EPITHELIUM (EPITHELIUM MUCOSAE)
Microvilli projecting from the mucosal epithelial cells
form a dense border that considerably increases the
absorptive intestinal surface area. Thus, the internal lin-
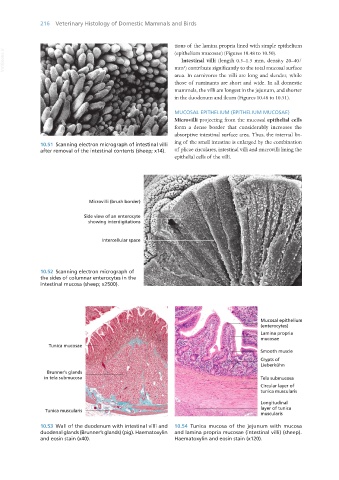
10.51 Scanning electron micrograph of intestinal villi ing of the small intestine is enlarged by the combination
after removal of the intestinal contents (sheep; x14). of plicae circulares, intestinal villi and microvilli lining the
epithelial cells of the villi.
10.52 Scanning electron micrograph of
the sides of columnar enterocytes in the
intestinal mucosa (sheep; x2500).
10.53 Wall of the duodenum with intestinal villi and 10.54 Tunica mucosa of the jejunum with mucosa
duodenal glands (Brunner’s glands) (pig). Haematoxylin and lamina propria mucosae (intestinal villi) (sheep).
and eosin stain (x40). Haematoxylin and eosin stain (x120).
Vet Histology.indb 216 16/07/2019 15:01