Page 25 - Veterinary Histology of Domestic Mammals and Birds, 5th Edition
P. 25
The cell (cellula) 7
(vacuoles). The internalised vesicles, which can reach 250 100% of their cell surface in the form of vesicles within
VetBooks.ir nm in diameter, are referred to as phagosomes (Figure 1.6). a period of half an hour. Since this does not alter the
Phagocytosis is predominantly performed by specialised surface of the volume of the cell, it follows that the
cells (phagocytes), particularly cells of the mononuclear vesicles are extensively recycled, and reincorporated
phagocytic system (MPS). into the cell membrane. Membrane-associated release
Phagocytosis is typically a receptor-mediated process of materials by the cell is also part of this recycling
in which cell surface receptors recognise antibody frag- process.
ments associated with invading microorganisms or cells. In most cases, vesicles formed by endocytosis enter the
In the cell-mediated immune response, for example (see endosomal system (see below). In some cases, endocytotic
Chapter 8, ‘Immune system and lymphatic organs’), bac- vesicles are transported through the cell and released at
teria become coated with antibody molecules that are another surface, without undergoing alteration. This pro-
recognised by receptors on macrophages. Binding of the cess is referred to as transcytosis (cytopempsis).
antibody with the receptor stimulates the cell to engulf
and phagocytose the microorganism. EXOCYTOSIS
In addition, phagocytes have the capacity to take up The mechanism of exocytosis is similar to that of endo-
non-biological materials (e.g. inhaled pollutants) and cell cytosis but occurs in the opposite direction. Cellular
fragments (e.g. from wounds, sites of inflammation and products are packaged into vesicles within the cell and
cell degeneration) without the involvement of receptors. transported to the surface. The vesicles fuse with the
Phagocytosis is usually associated with a reorganisation plasmalemma and deposit their contents into the sur-
of intracellular actin filaments. Ingestion of substances by rounding medium. After fusion of the exocytotic vesicle
phagocytosis is thus a clathrin-independent actin-depend- with the plasmalemma, the membrane associated with
ent form of endocytosis. the vesicle is reintroduced into the cytoplasm in a subse-
Vesicle formation occurs at varying rates in differ- quent endocytotic event. Two exocytotic pathways are
ent cells. Macrophages are capable of internalising recognised:
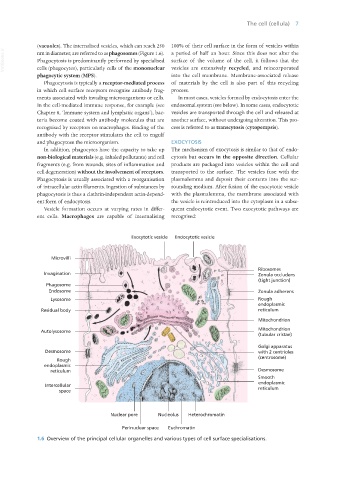
1.6 Overview of the principal cellular organelles and various types of cell surface specialisations.
Vet Histology.indb 7 16/07/2019 14:52