Page 362 - Veterinary Histology of Domestic Mammals and Birds, 5th Edition
P. 362
344 Veterinary Histology of Domestic Mammals and Birds
In chickens and turkeys, a bursa (bursa sterni) is
· provision of a barrier against irradiation and mecha-
VetBooks.ir · thermoregulation and located within the subcutis over the cranial aspect of the
nical, thermal, chemical and biological influences,
sternum. This frequently becomes pathologically enlarged
in broilers and laying hens housed under inappropriate
· communication.
conditions.
The lack of nerves in feathered skin,
In addition, the feathers are fundamental in enabling flight. except in the vicinity of feather follicles, renders this tissue
Where feathers are present, the skin is relatively relatively insensitive.
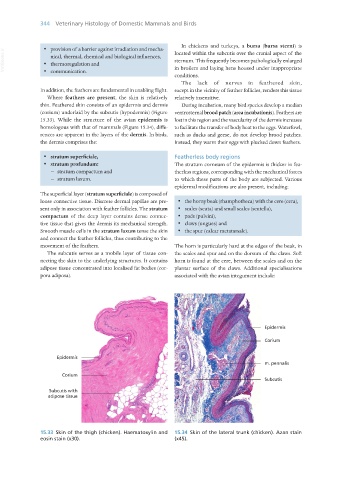
thin. Feathered skin consists of an epidermis and dermis During incubation, many bird species develop a median
(corium) underlaid by the subcutis (hypodermis) (Figure ventrosternal brood patch (area incubationis). Feathers are
15.33). While the structure of the avian epidermis is lost in this region and the vascularity of the dermis increases
homologous with that of mammals (Figure 15.34), diffe- to facilitate the transfer of body heat to the eggs. Waterfowl,
rences are apparent in the layers of the dermis. In birds, such as ducks and geese, do not develop brood patches.
the dermis comprises the: Instead, they warm their eggs with plucked down feathers.
· stratum superficiale, Featherless body regions
· stratum profundum: The stratum corneum of the epidermis is thicker in fea-
− stratum compactum and therless regions, corresponding with the mechanical forces
− stratum laxum. to which these parts of the body are subjected. Various
epidermal modifications are also present, including:
The superficial layer (stratum superficiale) is composed of
loose connective tissue. Discrete dermal papillae are pre- · the horny beak (rhamphotheca) with the cere (cera),
sent only in association with feather follicles. The stratum · scales (scuta) and small scales (scutella),
compactum of the deep layer contains dense connec- · pads (pulvini),
tive tissue that gives the dermis its mechanical strength. · claws (ungues) and
Smooth muscle cells in the stratum laxum tense the skin · the spur (calcar metatarsale).
and connect the feather follicles, thus contributing to the
movement of the feathers. The horn is particularly hard at the edges of the beak, in
The subcutis serves as a mobile layer of tissue con- the scales and spur and on the dorsum of the claws. Soft
necting the skin to the underlying structures. It contains horn is found at the cere, between the scales and on the
adipose tissue concentrated into localised fat bodies (cor- plantar surface of the claws. Additional specialisations
pora adiposa). associated with the avian integument include:
15.33 Skin of the thigh (chicken). Haematoxylin and 15.34 Skin of the lateral trunk (chicken). Azan stain
eosin stain (x30). (x45).
Vet Histology.indb 344 16/07/2019 15:06