Page 357 - Veterinary Histology of Domestic Mammals and Birds, 5th Edition
P. 357
Common integument (integumentum commune) 339
Hormonal regulation of the mammary gland oxytocin. This hormone, originating from the neurohy-
VetBooks.ir Development of the mammary gland and secretion of pophysis (see Chapter 9, ‘Endocrine system’), promotes
milk is largely under hormonal control. Oestrogens contraction of myoepithelial cells that surround the alveoli
induce development of the duct system. Development and parts of the excretory duct system. Hormones that
and growth of the secretory end pieces (alveoli) occurs regulate metabolism (e.g. thyroxin, growth hormone) also
under the influence of progesterone. During pregnancy, have a stimulatory effect on the mammary gland.
the inhibitory effect of oestrogen on prolactin suppresses
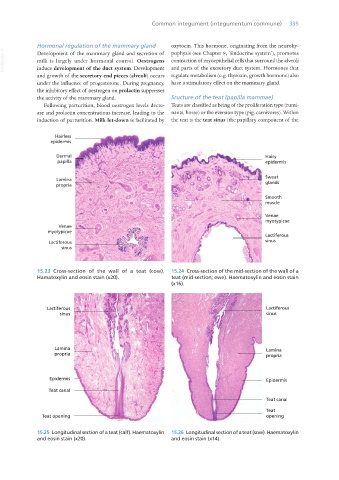
the activity of the mammary gland. Sructure of the teat (papilla mammae)
Following parturition, blood oestrogen levels decre- Teats are classified as being of the proliferation type (rumi-
ase and prolactin concentrations increase, leading to the nants, horse) or the eversion type (pig, carnivores). Within
induction of parturition. Milk let-down is facilitated by the teat is the teat sinus (the papillary component of the
Hairless
epidermis
Dermal
papilla
Lamina
propria
Venae
myotypicae
Lactiferous
sinus
15.23 Cross-section of the wall of a teat (cow). 15.24 Cross-section of the mid-section of the wall of a
Hamatoxylin and eosin stain (x20). teat (mid-section; ewe). Haematoxylin and eosin stain
(x16).
15.25 Longitudinal section of a teat (calf). Haematoxylin 15.26 Longitudinal section of a teat (sow). Haematoxylin
and eosin stain (x20). and eosin stain (x14).
Vet Histology.indb 339 16/07/2019 15:06