Page 355 - Veterinary Histology of Domestic Mammals and Birds, 5th Edition
P. 355
Common integument (integumentum commune) 337
VetBooks.ir
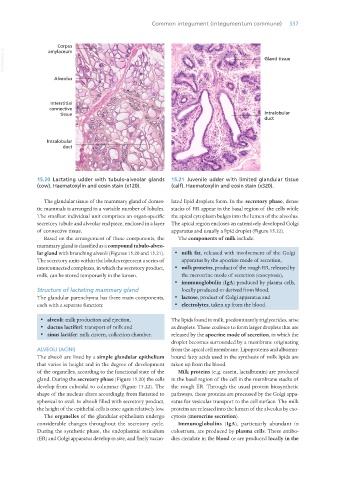
15.20 Lactating udder with tubulo-alveolar glands 15.21 Juvenile udder with limited glandular tissue
(cow). Haematoxylin and eosin stain (x120). (calf). Haematoxylin and eosin stain (x320).
The glandular tissue of the mammary gland of domes- lated lipid droplets form. In the secretory phase, dense
tic mammals is arranged in a variable number of lobules. stacks of ER appear in the basal region of the cells while
The smallest individual unit comprises an organ-specific the apical cytoplasm bulges into the lumen of the alveolus.
secretory tubule and alveolar end piece, enclosed in a layer The apical region encloses an extensively developed Golgi
of connective tissue. apparatus and usually a lipid droplet (Figure 15.22).
Based on the arrangement of these components, the The components of milk include:
mammary gland is classified as a compound tubulo-alveo-
lar gland with branching alveoli (Figures 15.20 and 15.21). · milk fat, released with involvement of the Golgi
The secretory units within the lobules represent a series of apparatus by the apocrine mode of secretion,
interconnected complexes, in which the secretory product, · milk proteins, product of the rough ER, released by
milk, can be stored temporarily in the lumen. the merocrine mode of secretion (exocytosis),
· immunoglobulin (IgA) produced by plasma cells,
Structure of lactating mammary gland locally produced or derived from blood,
The glandular parenchyma has three main components, · lactose, product of Golgi apparatus and
each with a separate function: · electrolytes, taken up from the blood.
· alveoli: milk production and ejection, The lipids found in milk, predominantly triglycerides, arise
· ductus lactiferi: transport of milk and as droplets. These coalesce to form larger droplets that are
· sinus lactifer: milk cistern, collection chamber. released by the apocrine mode of secretion, in which the
droplet becomes surrounded by a membrane originating
ALVEOLI (ACINI) from the apical cell membrane. Lipoproteins and albumin-
The alveoli are lined by a simple glandular epithelium bound fatty acids used in the synthesis of milk lipids are
that varies in height and in the degree of development taken up from the blood.
of the organelles, according to the functional state of the Milk proteins (e.g. casein, lactalbumin) are produced
gland. During the secretory phase (Figure 15.20) the cells in the basal region of the cell in the membrane stacks of
develop from cuboidal to columnar (Figure 15.22). The the rough ER. Through the usual protein biosynthetic
shape of the nucleus alters accordingly, from flattened to pathways, these proteins are processed by the Golgi appa-
spherical to oval. In alveoli filled with secretory product, ratus for vesicular transport to the cell surface. The milk
the height of the epithelial cells is once again relatively low. proteins are released into the lumen of the alveolus by exo-
The organelles of the glandular epithelium undergo cytosis (merocrine secretion).
considerable changes throughout the secretory cycle. Immunoglobulins (IgA), particuarly abundant in
During the synthetic phase, the endoplasmic reticulum colostrum, are produced by plasma cells. These antibo-
(ER) and Golgi apparatus develop in size, and finely vacuo- dies circulate in the blood or are produced locally in the
Vet Histology.indb 337 16/07/2019 15:06