Page 351 - Veterinary Histology of Domestic Mammals and Birds, 5th Edition
P. 351
Common integument (integumentum commune) 333
results from diffusion of nutrients across the intercellular Sebaceous and sweat glands arise together with hair fol-
VetBooks.ir space. The capillaries drain into venules and veins that licles from the epidermal anlage and become embedded in
ultimately join the subcutaneous venous network.
the tissue beneath. Thus, a ‘triad’ of epidermal structures
Hair (pili) and hair follicles – hair, sweat glands and sebaceous glands – is formed.
In certain regions of the body, elements of the triad
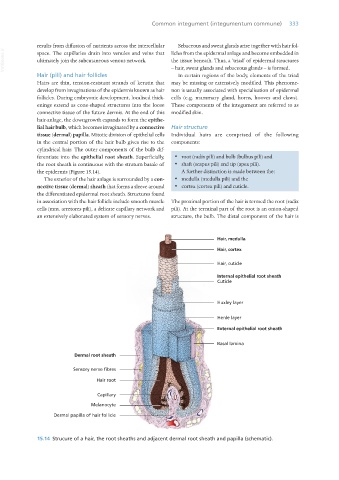
Hairs are thin, tension-resistant strands of keratin that may be missing or extensively modified. This phenome-
develop from invaginations of the epidermis known as hair non is usually associated with specialisation of epidermal
follicles. During embryonic development, localised thick- cells (e.g. mammary gland, horns, hooves and claws).
enings extend as cone-shaped structures into the loose These components of the integument are referred to as
connective tissue of the future dermis. At the end of this modified skin.
hair-anlage, the downgrowth expands to form the epithe-
lial hair bulb, which becomes invaginated by a connective Hair structure
tissue (dermal) papilla. Mitotic division of epithelial cells Individual hairs are comprised of the following
in the central portion of the hair bulb gives rise to the components:
cylindrical hair. The outer components of the bulb dif-
ferentiate into the epithelial root sheath. Superficially, · root (radix pili) and bulb (bulbus pili) and
the root sheath is continuous with the stratum basale of · shaft (scapus pili) and tip (apex pili).
the epidermis (Figure 15.14). A further distinction is made between the:
The exterior of the hair anlage is surrounded by a con- · medulla (medulla pili) and the
nective tissue (dermal) sheath that forms a sleeve around · cortex (cortex pili) and cuticle.
the differentiated epidermal root sheath. Structures found
in association with the hair follicle include smooth muscle The proximal portion of the hair is termed the root (radix
cells (mm. arretores pili), a delicate capillary network and pili). At the terminal part of the root is an onion-shaped
an extensively elaborated system of sensory nerves. structure, the bulb. The distal component of the hair is
15.14 Strucure of a hair, the root sheaths and adjacent dermal root sheath and papilla (schematic).
Vet Histology.indb 333 16/07/2019 15:06