Page 52 - Veterinary Histology of Domestic Mammals and Birds, 5th Edition
P. 52
34 Veterinary Histology of Domestic Mammals and Birds
VetBooks.ir · direct contacts:
− interdigitations and
· indirect contacts:
− occluding junctions (zonula occludens, tight
junction),
− anchoring junctions (zonula adherens, macula
adherens [desmosome]) and
− communication junctions (gap junction, nexus).
Direct contacts
The lateral and basal cell surfaces of many epithelial cells
exhibit irregularly developed folds and invaginations that
form interdigitations or interleaving zipper-like connec-
tions between neighbouring cells.
These are particularly pronounced in surface epithe-
lia associated with intensive ion exchange (e.g. cells of
proximal renal tubules or the cells of the striated [secre-
tory] duct of salivary glands). The plasmalemma projects
into the cell in the form of irregular, often elongated
infoldings. The lateral and particularly basal surface area
available for molecular transport is thus considerably
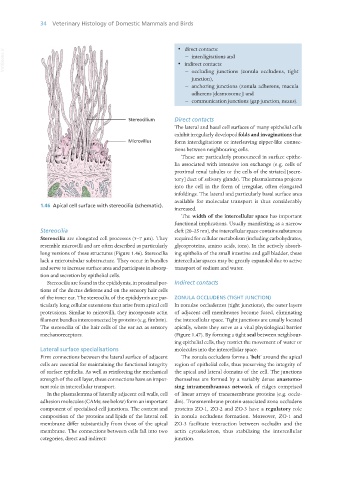
1.46 Apical cell surface with stereocilia (schematic).
increased.
The width of the intercellular space has important
functional implications. Usually manifesting as a narrow
Stereocilia cleft (20–25 nm), the intercellular space contains substances
Stereocilia are elongated cell processes (5–7 μm). They required for cellular metabolism (including carbohydrates,
resemble microvilli and are often described as particularly glycoproteins, amino acids, ions). In the actively absorb-
long versions of these structures (Figure 1.46). Stereocilia ing epithelia of the small intestine and gall bladder, these
lack a microtubular substructure. They occur in bundles intercellular spaces may be greatly expanded due to active
and serve to increase surface area and participate in absorp- transport of sodium and water.
tion and secretion by epithelial cells.
Stereocilia are found in the epididymis, in proximal por- Indirect contacts
tions of the ductus deferens and on the sensory hair cells
of the inner ear. The stereocilia of the epididymis are par- ZONULA OCCLUDENS (TIGHT JUNCTION)
ticularly long cellular extensions that arise from apical cell In zonulae occludentes (tight junctions), the outer layers
protrusions. Similar to microvilli, they incorporate actin of adjacent cell membranes become fused, eliminating
filament bundles interconnected by proteins (e.g. fimbrin). the intercellular space. Tight junctions are usually located
The stereocilia of the hair cells of the ear act as sensory apically, where they serve as a vital physiological barrier
mechanoreceptors. (Figure 1.47). By forming a tight seal between neighbour-
ing epithelial cells, they restrict the movement of water or
Lateral surface specialisations molecules into the intercellular space.
Firm connections between the lateral surface of adjacent The zonula occludens forms a ‘belt’ around the apical
cells are essential for maintaining the functional integrity region of epithelial cells, thus preserving the integrity of
of surface epithelia. As well as reinforcing the mechanical the apical and lateral domains of the cell. The junctions
strength of the cell layer, these connections have an impor- themselves are formed by a variably dense anastomo-
tant role in intercellular transport. sing intramembranous network of ridges comprised
In the plasmalemma of laterally adjacent cell walls, cell of linear arrays of transmembrane proteins (e.g. occlu-
adhesion molecules (CAMs; see below) form an important din). Transmembrane protein-associated zona occludens
component of specialised cell junctions. The content and proteins ZO-1, ZO-2 and ZO-3 have a regulatory role
composition of the proteins and lipids of the lateral cell in zonula occludens formation. Moreover, ZO-1 and
membrane differ substantially from those of the apical ZO-3 facilitate interaction between occludin and the
membrane. The connections between cells fall into two actin cytoskeleton, thus stabilising the intercellular
categories, direct and indirect: junction.
Vet Histology.indb 34 16/07/2019 14:54