Page 62 - Veterinary Histology of Domestic Mammals and Birds, 5th Edition
P. 62
44 Veterinary Histology of Domestic Mammals and Birds
VetBooks.ir
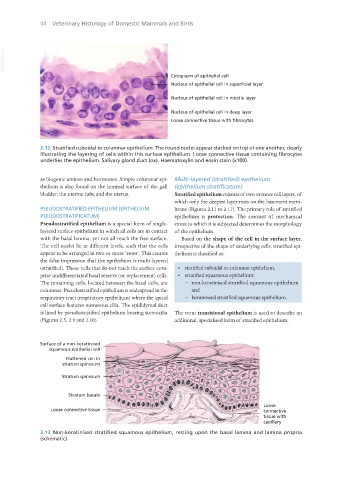
2.12 Stratified cuboidal to columnar epithelium. The round nuclei appear stacked on top of one another, clearly
illustrating the layering of cells within this surface epithelium. Loose connective tissue containing fibrocytes
underlies the epithelium. Salivary gland duct (ox). Haematoxylin and eosin stain (x100).
as biogenic amines and hormones. Simple columnar epi- Multi-layered (stratified) epithelium
thelium is also found on the luminal surface of the gall (epithelium stratificatum)
bladder, the uterine tube and the uterus. Stratified epithelium consists of two or more cell layers, of
which only the deepest layer rests on the basement mem-
PSEUDOSTRATIFIED EPITHELIUM (EPITHELIUM brane (Figures 2.11 to 2.17). The primary role of stratified
PSEUDOSTRATIFICATUM) epithelium is protection. The amount of mechanical
Pseudostratified epithelium is a special form of single- stress to which it is subjected determines the morphology
layered surface epithelium in which all cells are in contact of the epithelium.
with the basal lamina, yet not all reach the free surface. Based on the shape of the cell in the surface layer,
The cell nuclei lie at different levels, such that the cells irrespective of the shape of underlying cells, stratified epi-
appear to be arranged in two or more ‘rows’. This creates thelium is classified as:
the false impression that the epithelium is multi-layered
(stratified). Those cells that do not reach the surface com- • stratified cuboidal or columnar epithelium,
prise undifferentiated basal reserve (or replacement) cells. • stratified squamous epithelium:
The remaining cells, located between the basal cells, are − non-keratinised stratified squamous epithelium
columnar. Pseudostratified epithelium is widespread in the and
respiratory tract (respiratory epithelium) where the apical − keratinised stratified squamous epithelium.
cell surface features numerous cilia. The epididymal duct
is lined by pseudostratified epithelium bearing stereocilia The term transitional epithelium is used to describe an
(Figures 2.5, 2.9 and 2.10). additional, specialised form of stratified epithelium.
2.13 Non-keratinised stratified squamous epithelium, resting upon the basal lamina and lamina propria
(schematic).
Vet Histology.indb 44 16/07/2019 14:54