Page 63 - Veterinary Histology of Domestic Mammals and Birds, 5th Edition
P. 63
Epithelial tissue (textus epithelialis) 45
STRATIFIED CUBOIDAL OR COLUMNAR EPITHELIUM between the formation of a new cell in the stratum basale
VetBooks.ir COLUMNARE) through mitosis to its desquamation at the surface of the
(EPITHELIUM STRATIFICATUM CUBOIDEUM/
epithelium is generally 30 days.
Stratified cuboidal or columnar epithelium is found in rela-
In some regions, the protective function of stratified
tively few locations in the body. These include the lining of squamous epithelium is reinforced by the presence of basal
the larger excretory ducts of glands (e.g. parotid salivary epithelial pegs that interdigitate with papillae projecting
gland) (Figures 2.11 and 2.12). from the underlying connective tissue of the dermis to
form a particularly strong connection between these two
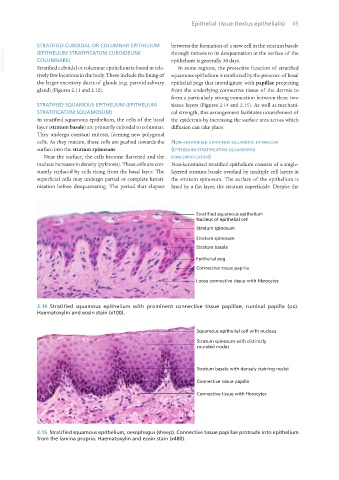
STRATIFIED SQUAMOUS EPITHELIUM (EPITHELIUM tissue layers (Figures 2.14 and 2.15). As well as mechani-
STRATIFICATUM SQUAMOSUM) cal strength, this arrangement facilitates nourishment of
In stratified squamous epithelium, the cells of the basal the epidermis by increasing the surface area across which
layer (stratum basale) are primarily cuboidal to columnar. diffusion can take place.
They undergo constant mitosis, forming new polygonal
cells. As they mature, these cells are pushed towards the non-keRatinised stRatified squamous ePithelium
surface into the stratum spinosum. (ePithelium stRatificatum squamosum
Near the surface, the cells become flattened and the noncoRnificatum)
nucleus increases in density (pyknosis). These cells are con- Non-keratinised stratified epithelium consists of a single-
stantly replaced by cells rising from the basal layer. The layered stratum basale overlaid by multiple cell layers in
superficial cells may undergo partial or complete kerati- the stratum spinosum. The surface of the epithelium is
nisation before desquamating. The period that elapses lined by a flat layer, the stratum superficiale. Despite the
2.14 Stratified squamous epithelium with prominent connective tissue papillae, ruminal papilla (ox).
Haematoxylin and eosin stain (x100).
2.15 Stratified squamous epithelium, oesophagus (sheep). Connective tissue papillae protrude into epithelium
from the lamina propria. Haematoxylin and eosin stain (x480).
Vet Histology.indb 45 16/07/2019 14:54