Page 67 - Veterinary Histology of Domestic Mammals and Birds, 5th Edition
P. 67
Epithelial tissue (textus epithelialis) 49
Table 2.1 Classification of surface epithelium based on morphology.
VetBooks.ir Epithelium Layering Occurrence
Squamous
Lining of body cavities (= serosa, mesothelium), lining of internal
Simple
surface of vessel walls (= endothelium), posterior corneal epithelium
Stratified a) keratinised, e.g. body surface (epidermis)
b) non-keratinised, e.g. oral cavity
Cuboidal Simple Many small ducts of glands, renal tubules, follicular epithelium of
the thyroid gland, germinal epithelium of the ovary.
Stratified Ducts of salivary glands.
Columnar Simple Non-ciliated, e.g. gastrointestinal tract, gall bladder; ciliated,
e.g. oviduct; non-ciliated pseudostratified, e.g. parts of ducts
of glands; ciliated pseudostratified, e.g. respiratory mucosa;
stereociliated, e.g. epididymal duct.
Stratified Large salivary gland ducts
Transitional Variable in height, e.g. renal pelvis, ureter, bladder and urethra
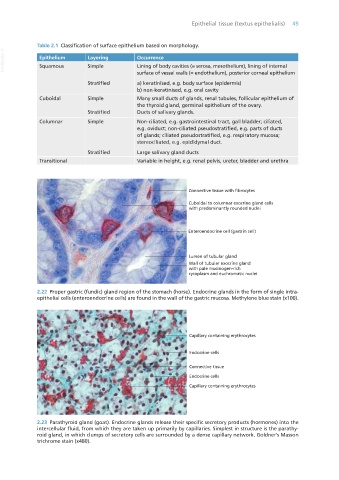
2.22 Proper gastric (fundic) gland region of the stomach (horse). Endocrine glands in the form of single intra-
epithelial cells (enteroendocrine cells) are found in the wall of the gastric mucosa. Methylene blue stain (x100).
2.23 Parathyroid gland (goat). Endocrine glands release their specific secretory products (hormones) into the
intercellular fluid, from which they are taken up primarily by capillaries. Simplest in structure is the parathy-
roid gland, in which clumps of secretory cells are surrounded by a dense capillary network. Goldner’s Masson
trichrome stain (x480).
Vet Histology.indb 49 16/07/2019 14:54