Page 154 - Zoo Animal Learning and Training
P. 154
138 Tasks for the Veterinary Assistant
(a) (b)
FIGURE 8.38 Restraining and occluding for IV: (a) saphenous and (b) femoral veins.
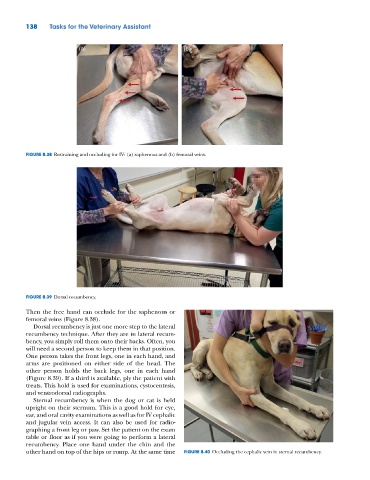
FIGURE 8.39 Dorsal recumbency.
Then the free hand can occlude for the saphenous or
femoral veins (Figure 8.38).
Dorsal recumbency is just one more step to the lateral
recumbency technique. After they are in lateral recum-
bency, you simply roll them onto their backs. Often, you
will need a second person to keep them in that position.
One person takes the front legs, one in each hand, and
arms are positioned on either side of the head. The
other person holds the back legs, one in each hand
(Figure 8.39). If a third is available, ply the patient with
treats. This hold is used for examinations, cystocentesis,
and ventrodorsal radiographs.
Sternal recumbency is when the dog or cat is held
upright on their sternum. This is a good hold for eye,
ear, and oral cavity examinations as well as for IV cephalic
and jugular vein access. It can also be used for radio-
graphing a front leg or paw. Set the patient on the exam
table or floor as if you were going to perform a lateral
recumbency. Place one hand under the chin and the
other hand on top of the hips or rump. At the same time FIGURE 8.40 Occluding the cephalic vein in sternal recumbency.