Page 29 - Veterinary Laser Therapy in Small Animal Practice
P. 29
Anti-inflammatory effect 15
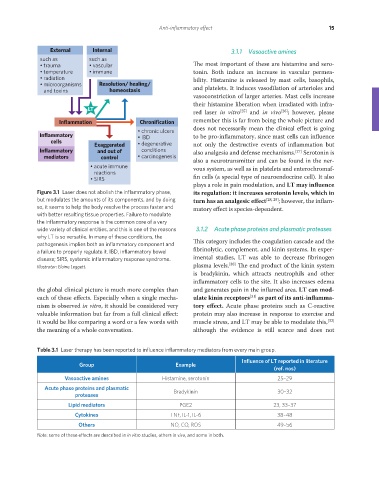
External Internal 3.1.1 Vasoactive amines
such as such as
• trauma • vascular The most important of these are histamine and sero-
• temperature • immune tonin. Both induce an increase in vascular permea-
• radiation bility. Histamine is released by mast cells, basophils,
• microorganisms Resolution/ healing/
• and toxins homeostasis and platelets. It induces vasodilation of arterioles and
vasoconstriction of larger arteries. Mast cells increase
their histamine liberation when irradiated with infra-
LT
red laser in vitro [25] and in vivo [26] ; however, please
Inflammation Chronification remember this is far from being the whole picture and
• chronic ulcers does not necessarily mean the clinical effect is going
Inflammatory • IBD to be pro-inflammatory, since mast cells can influence
cells Exaggerated • degenerative not only the destructive events of inflammation but
Inflammatory and out of • conditions also analgesia and defense mechanisms. [27] Serotonin is
mediators control • carcinogenesis also a neurotransmitter and can be found in the ner-
• acute immune vous system, as well as in platelets and enterochromaf-
• reactions
• SIRS fin cells (a special type of neuroendocrine cell). It also
plays a role in pain modulation, and LT may influence
Figure 3.1 Laser does not abolish the inflammatory phase, its regulation: it increases serotonin levels, which in
but modulates the amounts of its components, and by doing turn has an analgesic effect [28, 29] ; however, the inflam-
so, it seems to help the body resolve the process faster and matory effect is species-dependent.
with better resulting tissue properties. Failure to modulate
the inflammatory response is the common core of a very
wide variety of clinical entities, and this is one of the reasons 3.1.2 Acute phase proteins and plasmatic proteases
why LT is so versatile. In many of these conditions, the
pathogenesis implies both an inflammatory component and This category includes the coagulation cascade and the
a failure to properly regulate it. IBD, inflammatory bowel fibrinolytic, complement, and kinin systems. In exper-
disease; SIRS, systemic inflammatory response syndrome. imental studies, LT was able to decrease fibrinogen
Illustrator: Elaine Leggett. plasma levels. [30] The end product of the kinin system
is bradykinin, which attracts neutrophils and other
inflammatory cells to the site. It also increases edema
the global clinical picture is much more complex than and generates pain in the inflamed area. LT can mod-
each of these effects. Especially when a single mecha- ulate kinin receptors [31] as part of its anti-inflamma-
nism is observed in vitro, it should be considered very tory effect. Acute phase proteins such as C-reactive
valuable information but far from a full clinical effect: protein may also increase in response to exercise and
it would be like comparing a word or a few words with muscle stress, and LT may be able to modulate this, [32]
the meaning of a whole conversation. although the evidence is still scarce and does not
Table 3.1 Laser therapy has been reported to influence inflammatory mediators from every main group.
Influence of LT reported in literature
Group Example
(ref. nos)
Vasoactive amines Histamine, serotonin 25–29
Acute phase proteins and plasmatic
proteases Bradykinin 30–32
Lipid mediators PGE2 23, 33–37
Cytokines TNF, IL-1, IL-6 38–48
Others NO, CO, ROS 49–56
Note: some of these effects are described in in vitro studies, others in vivo, and some in both.
REDONDO PRINT (4-COL BLEED).indd 15 08/08/2019 09:46