Page 30 - Veterinary Laser Therapy in Small Animal Practice
P. 30
16 Veterinary Laser Therapy in Small Animal Practice
include other acute phase markers such as serum amy- consumers. Its expression is positively correlated with
loid A or P. histological grade, infiltration, and staging of tumors.
There is debate about COX-3: it has been suggested
3.1.3 Lipid mediators that this form is more commonly found in vascular
and central nervous system (CNS) tissues and may
These are the targets for most anti-inflammatory treat- be the target for paracetamol. But before you think
ments, both with steroids and NSAIDs. This group about getting rid of all COX-2, remember it also has
includes platelet activating factor (PAF) and arachi- physiological functions. You may actually remember a
donic acid (AA) derivatives or eicosanoids such as famous drug that exclusively inhibited COX-2 and was
thromoboxane A (TXA ), prostacyclin (PGI ), and sold as a super-aspirin, but had to be removed from
2
2
2
leukotriene B (LTB ). AA is part of the cell membrane, the market due to cardiovascular risks. Now, how is
4
4
from where the enzyme phospholipase A (PLA ) all this related to LT? Several studies have reported a
2
2
detaches it. Once free, AA can be metabolized via pros- decrease in COX-2 activity and prostaglandin produc-
taglandin-endoperoxide synthase, more commonly tion at the inflammation site and in the blood and CNS
known as cyclooxygenase (COX), to form prostanoids after LT [23, 33–37] ; this is probably one of the main anti-
(prostaglandins, prostacyclins, and thromboxanes) inflammatory effects that also influences analgesia. To
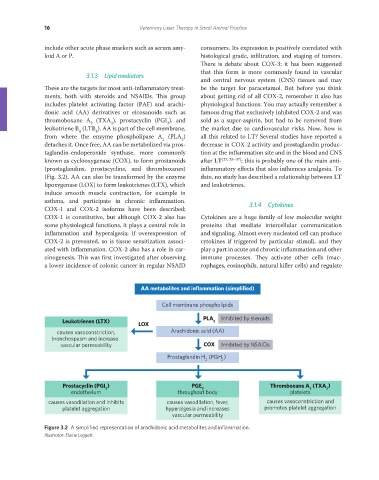
(Fig. 3.2). AA can also be transformed by the enzyme date, no study has described a relationship between LT
lipoxygenase (LOX) to form leukotrienes (LTX), which and leukotrienes.
induce smooth muscle contraction, for example in
asthma, and participate in chronic inflammation. 3.1.4 Cytokines
COX-1 and COX-2 isoforms have been described;
COX-1 is constitutive, but although COX-2 also has Cytokines are a huge family of low molecular weight
some physiological functions, it plays a central role in proteins that mediate intercellular communication
inflammation and hyperalgesia; if overexpression of and signaling. Almost every nucleated cell can produce
COX-2 is prevented, so is tissue sensitization associ- cytokines if triggered by particular stimuli, and they
ated with inflammation. COX-2 also has a role in car- play a part in acute and chronic inflammation and other
cinogenesis. This was first investigated after observing immune processes. They activate other cells (mac-
a lower incidence of colonic cancer in regular NSAID rophages, eosinophils, natural killer cells) and regulate
AA metabolites and inflammation (simplified)
Cell membrane phospholipids
Leukotrienes (LTX) PLA 2 Inhibited by steroids
LOX
causes vasoconstriction, Arachidonic acid (AA)
bronchospasm and increase
vascular permeability COX Inhibited by NSAIDs
Prostaglandin H (PGH )
2 2
Prostacyclin (PGI ) PGE Thromboxane A (TXA )
2
endothelium 2 throughout body platelets 2 2
causes vasodilation and inhibits causes vasodilation, fever, causes vasoconstriction and
platelet aggregation hyperalgesia and increases promotes platelet aggregation
vascular permeability
Figure 3.2 A simplified representation of arachidonic acid metabolites and inflammation.
Illustrator: Elaine Leggett.
REDONDO PRINT (4-COL BLEED).indd 16 08/08/2019 09:46