Page 31 - Veterinary Laser Therapy in Small Animal Practice
P. 31
Anti-inflammatory effect 17
cell survival, multiplication and apoptosis, tissue repair, permeability, activate coagulation and lymphocytes,
and malignant transformation. attract neutrophils, and stimulate the liver to release
Regulation of cytokines is a fine piece of art, a really acute phase proteins such as amyloid A and C-reactive
intricate net, since they may show properties such as protein. The main pro-inflammatory cytokines are IL-1
antagonism, synergy, and pleiotropy – i.e. the same and TNF-α, which may act synergistically. Regulation
cytokine can have different effects on different cell lines of IL-1 activity occurs naturally via the receptor antag-
(like a word can have different meanings depending on onist (IL-1RA), which blocks the IL-1 receptor but does
the context). They are also involved in downregulation not generate IL-1 activity. IL-1 and TNF-α are released
mechanisms, in which the production of one cytokine by macrophages and other cell types; they start the
stimulates the release of other cytokines with the oppo- inflammatory response when they contact the endo-
site effect. thelium, recruit leukocytes, and induce COX-2 syn-
Some cytokines have kept their original names, for thesis, and are responsible for systemic inflammatory
instance transforming growth factor (TGF) and tumor reactions. On the other hand, they promote fibroblast
necrosis factor (TNF), while others are named interleu- multiplication and collagen synthesis in the tissue
kins (IL). Some of them promote inflammation (IL-1, repair phase, but with LT we can achieve this without
IL-6, IL-8, TNF-α), while others are anti-inflammatory the pro-inflammatory effect. IL-6 also increases during
agents (IL-4, IL-10, IL-13, TGF-β). Many of the anti- inflammation in proportion to the degree and duration
inflammatory effects of LT are due to the shift in that of inflammation, and therefore acts as a diagnostic and
balance, since it decreases the levels of pro-inflamma- prognostic indicator, but is also involved in the activa-
tory cytokines, while promoting expression of the anti- tion of anti-inflammatory mechanisms.
inflammatory ones (Figs 3.3 and 3.4). The decrease in IL-1, TNF, and IL-6 after LT has
Pro-inflammatory cytokines increase vascular been described in vitro with different cell lines [38] and
(a) (b)
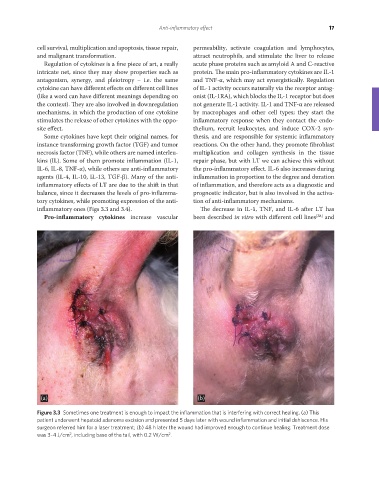
Figure 3.3 Sometimes one treatment is enough to impact the inflammation that is interfering with correct healing. (a) This
patient underwent hepatoid adenoma excision and presented 5 days later with wound inflammation and initial dehiscence. His
surgeon referred him for a laser treatment; (b) 48 h later the wound had improved enough to continue healing. Treatment dose
was 3–4 J/cm , including base of the tail, with 0.2 W/cm .
2
2
REDONDO PRINT (4-COL BLEED).indd 17 08/08/2019 09:46