Page 14 - HPB Handbook - May 30 2022 (Flipbook) v2
P. 14
Page 14 of 22
Regimens
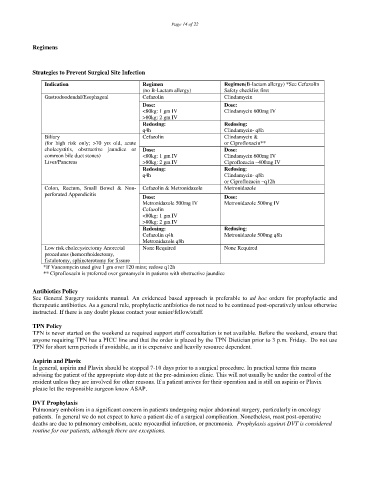
Strategies to Prevent Surgical Site Infection
Indication Regimen Regimen(B-lactam allergy) *See Cefazolin
(no B-Lactam allergy) Safety checklist first
Gastroduodendal/Esophageal Cefazolin Clindamycin
Dose: Dose:
<80kg: 1 gm IV Clindamycin 600mg IV
>80kg: 2 gm IV
Redosing: Redosing:
q4h Clindamycin- q8h
Biliary Cefazolin Clindamycin &
(for high risk only; >70 yrs old, acute or Ciprofloxacin**
cholecystitis, obstructive jaundice or Dose: Dose:
common bile duct stones) <80kg: 1 gm IV Clindamycin 600mg IV
Liver/Pancreas >80kg: 2 gm IV Ciproflozacin –400mg IV
Redosing: Redosing:
q4h Clindamycin- q8h
or Ciproflozacin –q12h
Colon, Rectum, Small Bowel & Non- Cefazolin & Metronidazole Metronidazole
perforated Appendicitis
Dose: Dose:
Metronidazole 500mg IV Metronidazole 500mg IV
Cefazolin
<80kg: 1 gm IV
>80kg: 2 gm IV
Redosing: Redosing:
Cefazolin q4h Metronidazole 500mg q8h
Metronidazole q8h
Low risk cholecystectomy Anorectal None Required None Required
procedures (hemorrhoidectomy,
fistulotomy, sphincterotomy for fissure
*If Vancomycin used give 1 gm over 120 mins; redose q12h
** Ciprofloxacin is preferred over gentamycin in patients with obstructive jaundice
Antibiotics Policy
See General Surgery residents manual. An evidenced based approach is preferable to ad hoc orders for prophylactic and
therapeutic antibiotics. As a general rule, prophylactic antibiotics do not need to be continued post-operatively unless otherwise
instructed. If there is any doubt please contact your senior/fellow/staff.
TPN Policy
TPN is never started on the weekend as required support staff consultation is not available. Before the weekend, ensure that
anyone requiring TPN has a PICC line and that the order is placed by the TPN Dietician prior to 3 p.m. Friday. Do not use
TPN for short term periods if avoidable, as it is expensive and heavily resource dependent.
Aspirin and Plavix
In general, aspirin and Plavix should be stopped 7-10 days prior to a surgical procedure. In practical terms this means
advising the patient of the appropriate stop date at the pre-admission clinic. This will not usually be under the control of the
resident unless they are involved for other reasons. If a patient arrives for their operation and is still on aspirin or Plavix
please let the responsible surgeon know ASAP.
DVT Prophylaxis
Pulmonary embolism is a significant concern in patients undergoing major abdominal surgery, particularly in oncology
patients. In general we do not expect to have a patient die of a surgical complication. Nonetheless, most post-operative
deaths are due to pulmonary embolism, acute myocardial infarction, or pneumonia. Prophylaxis against DVT is considered
routine for our patients, although there are exceptions.