Page 87 - Financial Statement Analysis
P. 87
sub79433_ch01.qxd 4/7/08 11:21 AM Page 64
64 Financial Statement Analysis
CASE 1–8
Comparative Analysis Colgate and Kimberly-Clark
Kimberly-Clark is a household products company that produces and sells various paper products
under popular brand names such as Kleenex and Scott. In many respects, Kimberly-Clark is sim-
ilar to Colgate: both are mature and profitable consumer products’ companies that are of similar
size. Therefore, Kimberly-Clark is a good company to compare Colgate’s financial performance
with. Refer to select financial information about Colgate over the 1996–2006 period reproduced
in Exhibit 1.3. The table below provides identical information relating to Kimberly-Clark over the
same period.
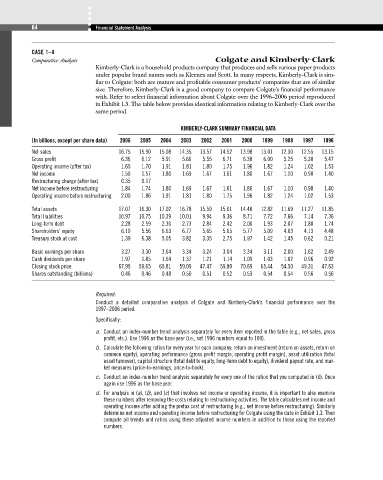
KIMBERLY-CLARK SUMMARY FINANCIAL DATA
(In billions, except per share data) 2006 2005 2004 2003 2002 2001 2000 1999 1998 1997 1996
Net sales 16.75 15.90 15.08 14.35 13.57 14.52 13.98 13.01 12.30 12.55 13.15
Gross profit 6.36 6.12 5.91 5.66 5.55 6.71 6.38 6.00 5.25 5.30 5.47
Operating income (after tax) 1.65 1.70 1.91 1.81 1.80 1.75 1.96 1.82 1.24 1.02 1.53
Net income 1.50 1.57 1.80 1.69 1.67 1.61 1.80 1.67 1.10 0.90 1.40
Restructuring charge (after tax) 0.35 0.17
Net income before restructuring 1.84 1.74 1.80 1.69 1.67 1.61 1.80 1.67 1.10 0.90 1.40
Operating income before restructuring 2.00 1.86 1.91 1.81 1.80 1.75 1.96 1.82 1.24 1.02 1.53
Total assets 17.07 16.30 17.02 16.78 15.59 15.01 14.48 12.82 11.69 11.27 11.85
Total liabilities 10.97 10.75 10.39 10.01 9.94 9.36 8.71 7.72 7.66 7.14 7.36
Long-term debt 2.28 2.59 2.30 2.73 2.84 2.42 2.00 1.93 2.07 1.80 1.74
Shareholders’ equity 6.10 5.56 6.63 6.77 5.65 5.65 5.77 5.09 4.03 4.13 4.48
Treasury stock at cost 1.39 6.38 5.05 3.82 3.35 2.75 1.97 1.42 1.45 0.62 0.21
Basic earnings per share 3.27 3.30 3.64 3.34 3.24 3.04 3.34 3.11 2.00 1.62 2.49
Cash dividends per share 1.97 1.85 1.64 1.37 1.21 1.14 1.09 1.03 1.02 0.96 0.92
Closing stock price 67.95 59.65 65.81 59.09 47.47 59.80 70.69 65.44 54.50 49.31 47.63
Shares outstanding (billions) 0.46 0.46 0.48 0.50 0.51 0.52 0.53 0.54 0.54 0.56 0.56
Required:
Conduct a detailed comparative analysis of Colgate and Kimberly-Clark’s financial performance over the
1997–2006 period.
Specifically:
a. Conduct an index-number trend analysis separately for every item reported in the table (e.g., net sales, gross
profit, etc.). Use 1996 as the base year (i.e., set 1996 numbers equal to 100).
b. Calculate the following ratios for every year for each company: return on investment (return on assets, return on
common equity), operating performance (gross profit margin, operating profit margin), asset utilization (total
asset turnover), capital structure (total debt to equity, long-term debt to equity), dividend payout rate, and mar-
ket measures (price-to-earnings, price-to-book).
c. Conduct an index-number trend analysis separately for every one of the ratios that you computed in (b). Once
again use 1996 as the base year.
d. For analysis in (a), (b), and (c) that involves net income or operating income, it is important to also examine
these numbers after removing the costs relating to restructuring activities. The table calculates net income and
operating income after adding the pretax cost of restructuring (e.g., net income before restructuring). Similarly
determine net income and operating income before restructuring for Colgate using the data in Exhibit 1.3. Then
compute all trends and ratios using these adjusted income numbers in addition to those using the reported
numbers.