Page 37 - MHF-FeedingMinds-final.indd
P. 37
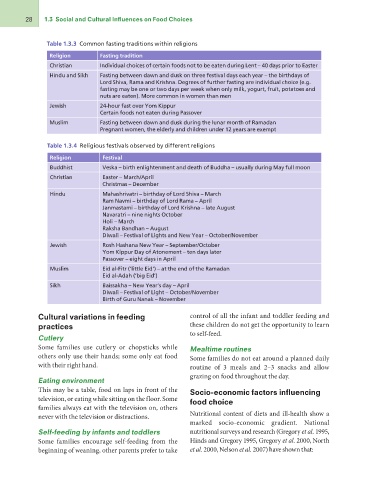
28 1.3 Social and Cultural Influences on Food Choices
Table 1.3.3 Common fasting traditions within religions
Religion Fasting tradition
Christian
Hindu and Sikh Individual choices of certain foods not to be eaten during Lent – 40 days prior to Easter
Jewish Fasting between dawn and dusk on three festival days each year – the birthdays of
Muslim Lord Shiva, Rama and Krishna. Degrees of further fasting are individual choice (e.g.
fasting may be one or two days per week when only milk, yogurt, fruit, potatoes and
nuts are eaten). More common in women than men
24-hour fast over Yom Kippur
Certain foods not eaten during Passover
Fasting between dawn and dusk during the lunar month of Ramadan
Pregnant women, the elderly and children under 12 years are exempt
Table 1.3.4 Religious festivals observed by different religions
Religion Festival
Buddhist
Christian Veska – birth enlightenment and death of Buddha – usually during May full moon
Hindu
Easter – March/April
Jewish Christmas – December
Muslim
Sikh Mahashrivatri – birthday of Lord Shiva – March
Ram Navmi – birthday of Lord Rama – April
Janmastami – birthday of Lord Krishna – late August
Navaratri – nine nights October
Holi – March
Raksha Bandhan – August
Diwali – Festival of Lights and New Year – October/November
Rosh Hashana New Year – September/October
Yom Kippur Day of Atonement – ten days later
Passover – eight days in April
Eid al-Fitr (‘little Eid’) – at the end of the Ramadan
Eid al-Adah (‘big Eid’)
Baissakha – New Year’s day – April
Diwali – Festival of Light – October/November
Birth of Guru Nanak – November
Cultural variations in feeding control of all the infant and toddler feeding and
practices these children do not get the opportunity to learn
to self-feed.
Cutlery
Some families use cutlery or chopsticks while Mealtime routines
others only use their hands; some only eat food Some families do not eat around a planned daily
with their right hand. routine of 3 meals and 2–3 snacks and allow
grazing on food throughout the day.
Eating environment
This may be a table, food on laps in front of the Socio-economic factors influencing
television, or eating while sitting on the floor. Some food choice
families always eat with the television on, others
never with the television or distractions. Nutritional content of diets and ill-health show a
marked socio-economic gradient. National
Self-feeding by infants and toddlers nutritional surveys and research (Gregory et al. 1995,
Some families encourage self-feeding from the Hinds and Gregory 1995, Gregory et al. 2000, North
beginning of weaning, other parents prefer to take et al. 2000, Nelson et al. 2007) have shown that: