Page 107 - Medicinal Chemistry Self Assessment
P. 107
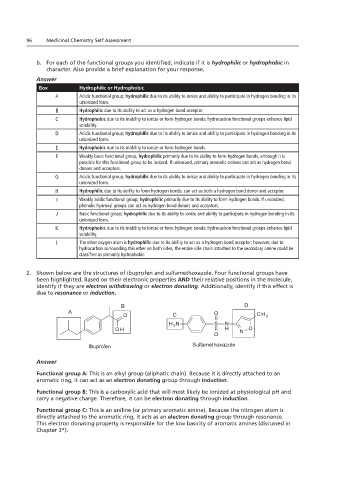
96 Medicinal Chemistry Self Assessment
b. For each of the functional groups you identified, indicate if it is hydrophilic or hydrophobic in
Structures for 1.1 and 2.1
character. Also provide a brief explanation for your response.
Answer
The bold has been removed. The exact same structures are in both of these chapters, but I have provided two
Box Hydrophilic or Hydrophobic
copies in the event you wanted that.
A
Acidic functional group; hydrophilic due to its ability to ionize and ability to participate in hydrogen bonding in its
unionized form.
B Hydrophilic due to its ability to act as a hydrogen bond acceptor.
C Hydrophobic due to its inability to ionize or form hydrogen bonds; hydrocarbon functional groups enhance lipid
solubility.
D A Acidic functional group; hydrophilic due to its ability to ionize and ability to participate in hydrogen bonding in its
unionized form. F
E Hydrophobic due to its inability to ionize or form hydrogen bonds.
C
F Weakly basic functional group; hydrophilic primarily due to its ability to form hydrogen bonds, although it is
possible for this functional group to be ionized. If unionized, primary aromatic amines can act as hydrogen bond
donors and acceptors. E
G Acidic functional group; hydrophilic due to its ability to ionize and ability to participate in hydrogen bonding in its
unionized form. D
Warfarin Hydrophilic due to its ability to form hydrogen bonds; can act as both a hydrogen bond donor and acceptor. G
H
Bromfenac
B
Phenytoin
I Weakly acidic functional group; hydrophilic primarily due to its ability to form hydrogen bonds. If unionized,
phenolic hydroxyl groups can act as hydrogen bond donors and acceptors.
J Basic functional group; hydrophilic due to its ability to ionize and ability to participate in hydrogen bonding in its
unionized form.
K Hydrophobic due to its inability to ionize or form hydrogen bonds; hydrocarbon functional groups enhance lipid
H solubility.
L The ether oxygen atom is hydrophilic due to its ability to act as a hydrogen bond acceptor; however, due to
J
K
L
I hydrocarbon surrounding this ether on both sides, the entire side chain attached to the secondary amine could be
classified as primarily hydrophobic.
Salmeterol
2. Shown below are the structures of ibuprofen and sulfamethoxazole. Four functional groups have
been highlighted. Based on their electronic properties AND their relative positions in the molecule,
identify if they are electron withdrawing or electron donating. Additionally, identify if this effect is
due to resonance or induction.
B D
A O
O C CH 3
H 2 N S N
OH H N O
O
Ibuprofen Sulfamethoxazole
Answer
Functional group A: This is an alkyl group (aliphatic chain). Because it is directly attached to an
aromatic ring, it can act as an electron donating group through induction.
Functional group B: This is a carboxylic acid that will most likely be ionized at physiological pH and
carry a negative charge. Therefore, it can be electron donating through induction.
Functional group C: This is an aniline (or primary aromatic amine). Because the nitrogen atom is
directly attached to the aromatic ring, it acts as an electron donating group through resonance.
This electron donating property is responsible for the low basicity of aromatic amines (discussed in
Chapter 3*).
Page 1 of 2