Page 111 - Medicinal Chemistry Self Assessment
P. 111
2.2
1. For each of the drugs or experimental drugs shown below, identify all of the acidic and basic functional
groups.
2
1
Bromfenac
Experimental oral anticoagulant
5
7 3 4
8
6
Sorbinil
100 Medicinal Chemistry Self Assessment Experimental antidiabetic agent
2. Using any one of the acidic functional groups that you identified in question 1, provide an explana-
Answer:
tion as to why the functional group is acidic. Also provide a similar type of analysis for any one of the
basic functional groups that you identified in question 1.
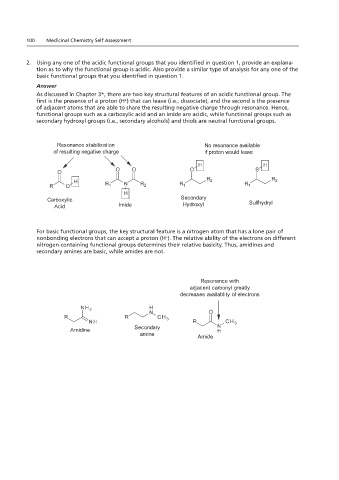
As discussed in Chapter 3*, there are two key structural features of an acidic functional group. The first is the
Answer
+
presence of a proton (H ) that can leave (i.e., dissociate), and the second is the presence of adjacent atoms that
As discussed in Chapter 3*, there are two key structural features of an acidic functional group. The
first is the presence of a proton (H ) that can leave (i.e., dissociate), and the second is the presence
+
acid and an imide are acidic, while functional groups such as secondary hydroxyl groups (i.e., secondary
of adjacent atoms that are able to share the resulting negative charge through resonance. Hence,
functional groups such as a carboxylic acid and an imide are acidic, while functional groups such as
alcohols) and thiols are neutral functional groups.
secondary hydroxyl groups (i.e., secondary alcohols) and thiols are neutral functional groups.
Resonance stabilization No resonance available
of resulting negative charge if proton would leave
Carboxylic Secondary Sulfhydryl
Acid Imide Hydroxyl
For basic functional groups, the key structural feature is a nitrogen atom that has a lone pair of
Page 1 of 5
+
nonbonding electrons that can accept a proton (H ). The relative ability of the electrons on different
nitrogen-containing functional groups determines their relative basicity. Thus, amidines and
secondary amines are basic, while amides are not.
For basic functional groups, the key structural feature is a nitrogen atom that has a lone pair of nonbonding
amides are not.
Resonance with
adjacent carbonyl greatly
decreases availablity of electrons
Amidine Secondary
amine Amide
3. Using the structures from question 1, modify all of the acidic functional groups to show their ionized forms and
in the table below identify the normal pKa range for the specific functional group.
Answer:
_
Experimental oral anticoagulant Bromfenac
_
Sorbinil
Experimental antidiabetic agent
Page 2 of 5