Page 141 - Medicinal Chemistry Self Assessment
P. 141
130 Medicinal Chemistry Self Assessment
Answer
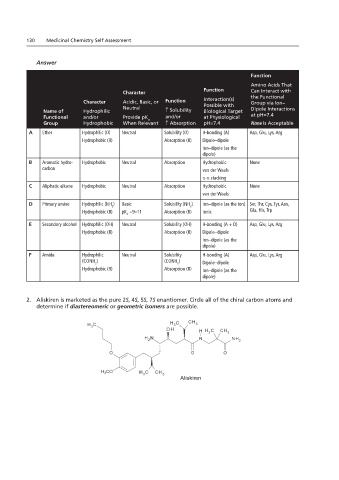
Function
Amino Acids That
Function Can Interact with
Character
Character Acidic, Basic, or Function Interaction(s) the Functional
Group via Ion–
Neutral Possible with Dipole Interactions
Name of Hydrophilic ↑ Solubility Biological Target
Functional and/or Provide pK and/or at Physiological at pH=7.4
a
Group Hydrophobic When Relevant ↑ Absorption pH=7.4 None Is Acceptable
A Ether Hydrophilic (O) Neutral Solubility (O) H-bonding (A) Asp, Glu, Lys, Arg
Hydrophobic (R) Absorption (R) Dipole–dipole
Ion–dipole (as the
dipole)
B Aromatic hydro- Hydrophobic Neutral Absorption Hydrophobic None
carbon van der Waals
π-π stacking
C Aliphatic alkane Hydrophobic Neutral Absorption Hydrophobic None
van der Waals
Medicinal Chemistry Self-Assessment Book: Batch Two
D Primary amine Hydrophilic (NH ) Basic Solubility (NH ) Ion–dipole (as the ion) Ser, Thr, Cys, Tyr, Asn,
2 Chapters 1.8 and 2.8
2
Hydrophobic (R) pK ~9–11 Absorption (R) Ionic Glu, His, Trp
a
Chapter 1.8/2.8 (remove bold from drug name x2)
E Secondary alcohol Hydrophilic (OH) Neutral Solubility (OH) H-bonding (A + D) Asp, Glu, Lys, Arg
Hydrophobic (R) Absorption (R) Dipole–dipole
E Ion–dipole (as the
D dipole) F
F Amide Hydrophilic A Neutral Solubility H-bonding (A) Asp, Glu, Lys, Arg
(CONH ) B (CONH ) Dipole–dipole
2
2
Hydrophobic (R) Absorption (R) Ion–dipole (as the
dipole)
Aliskiren
2. Aliskiren is marketed as the pure 2S, 4S, 5S, 7S enantiomer. Circle all of the chiral carbon atoms and
C
determine if diastereomeric or geometric isomers are possible.
Aliskiren