Page 149 - Medicinal Chemistry Self Assessment
P. 149
138 Medicinal Chemistry Self Assessment
Replacement structure for the answer to question 2 in Chapter 2.9 (Aripiprazole)
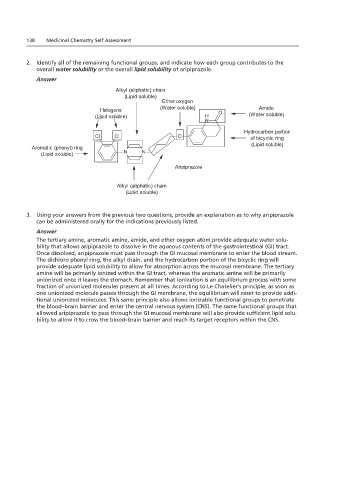
2. Identify all of the remaining functional groups, and indicate how each group contributes to the
overall water solubility or the overall lipid solubility of aripiprazole.
Answer
Alkyl (aliphatic) chain
(Lipid soluble)
Ether oxygen
Halogens (Water soluble) Amide
(Lipid soluble) (Water soluble)
Hydrocarbon portion
of bicyclic ring
(Lipid soluble)
Aromatic (phenyl) ring
(Lipid soluble)
Aripiprazole
Alkyl (aliphatic) chain
(Lipid soluble)
3. Using your answers from the previous two questions, provide an explanation as to why aripiprazole
Replacement structure for question 6 in BOTH Chapters 1.12 and 2.12 (Chlorpropamide and Other
can be administered orally for the indications previously listed.
Sulfonylureas)
Answer
The tertiary amine, aromatic amine, amide, and ether oxygen atom provide adequate water solu-
bility that allows aripiprazole to dissolve in the aqueous contents of the gastrointestinal (GI) tract.
Once dissolved, aripiprazole must pass through the GI mucosal membrane to enter the blood stream.
The dichloro phenyl ring, the alkyl chain, and the hydrocarbon portion of the bicyclic ring will
Cl
provide adequate lipid solubility to allow for absorption across the mucosal membrane. The tertiary
O
O
amine will be primarily ionized within the GI tract, whereas the aromatic amine will be primarily
O
unionized once it leaves the stomach. Remember that ionization is an equilibrium process with some
N
N
S
H
fraction of unionized molecules present at all times. According to Le Chatelier’s principle, as soon as
H
N
O
one unionized molecule passes through the GI membrane, the equilibrium will reset to provide addi-
H
O
tional unionized molecules. This same principle also allows ionizable functional groups to penetrate
C
H
Glyburide
the blood–brain barrier and enter the central nervous system (CNS). The same functional groups that
3
allowed aripiprazole to pass through the GI mucosal membrane will also provide sufficient lipid solu-
bility to allow it to cross the blood–brain barrier and reach its target receptors within the CNS.
O OH
O O
H 3 C S N N
N O H H
H
Metabolite of glyburide