Page 185 - Medicinal Chemistry Self Assessment
P. 185
E
174 Medicinal Chemistry Self Assessment C D
E
A D
C
• Functional Group E is a tertiary hydroxyl group. Based on its position in the molecule and the
A
fact that it is not directly attached to an aromatic ring, it acts as an electron withdrawing group
through induction. F
B
F
B
1. Using the se.
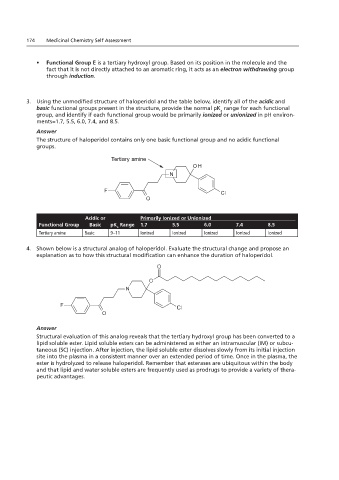
3. Using the unmodified structure of haloperidol and the table below, identify all of the acidic and
basic functional groups present in the structure, provide the normal pK range for each functional
2. Based on their electronic induction.
a
group, and identify if each functional group would be primarily ionized or unionized in pH environ-
1. Using the se.
3. Using the in pH environments of 1.7, 5.5, 6.0, 7.4, and 8.5.
ments=1.7, 5.5, 6.0, 7.4, and 8.5.
2. Based on their electronic induction.
Answer
Answer
3. Using the in pH environments of 1.7, 5.5, 6.0, 7.4, and 8.5.
The structure of haloperidol contains only one basic functional group and no acidic functional groups.
The structure of haloperidol contains only one basic functional group and no acidic functional
groups.
Answer
The structure of haloperidol contains only one basic functional group and no acidic functional groups.
Tertiary amine
OH
Tertiary amine N
OH
F N Cl
O
F
O Cl
Acidic or Primarily Ionized or Unionized
Functional Group Basic pK Range 1.7 5.5 6.0 7.4 8.5
a
4. Shown below is a structural analog can enhance the duration of haloperidol.
Tertiary amine Basic 9–11 Ionized Ionized Ionized Ionized Ionized
4. Shown below is a structural analog can enhance the duration of haloperidol.
4. Shown below is a structural analog of haloperidol. Evaluate the structural change and propose an
explanation as to how this structural modification can enhance the duration of haloperidol.
5. Using the table below ionizable functional groups.
Answer
Structural evaluation of this analog reveals that the tertiary hydroxyl group has been converted to a
lipid soluble ester. Lipid soluble esters can be administered as either an intramuscular (IM) or subcu-
5. Using the table below ionizable functional groups. C
taneous (SC) injection. After injection, the lipid soluble ester dissolves slowly from its initial injection
B
site into the plasma in a consistent manner over an extended period of time. Once in the plasma, the
ester is hydrolyzed to release haloperidol. Remember that esterases are ubiquitous within the body
C
D
and that lipid and water soluble esters are frequently used as prodrugs to provide a variety of thera-
B
peutic advantages. A
D
A