Page 189 - Medicinal Chemistry Self Assessment
P. 189
178 Medicinal Chemistry Self Assessment
Continued from previous page.
D Cycloalkane Hydrophobic Neutral Absorption Hydrophobic None
van der Waals
E Primary alcohol Hydrophilic (OH) Neutral Solubility (OH) H-bonding (A+D) Lys, Arg, Glu, Asp
Hydrophobic (R) Absorption (R) Dipole–dipole
Ion–dipole (as the
dipole)
F Tertiary alcohol Hydrophilic (OH) Neutral Solubility (OH) H-bonding (A+D) Lys, Arg, Glu, Asp
Hydrophobic (R) Absorption (R) Dipole–dipole
Ion–dipole (as the
dipole)
564
739
2. The glucocorticoids interact with residues within the glucocorticoid receptor (Arg , Asn , Thr ,
611
Gln , and Gln ) via hydrogen bonding and ion–dipole interactions at physiological pH (7.4). Iden-
642
570
tify which functional groups could interact with the side chains of these amino acids.
Answer
Can Interact with Can Interact with
564
Asparagine and Glutamine and
642
570
Threonine 739 via a Glutamine via a
Can Interact with Arginine Hydrogen Bonding Hydrogen Bonding
611
via an Ion–Dipole Interaction Interaction Interaction
Functional
Group Yes or No Yes or No Yes or No
Yes
A Yes 1.17 and 2.17 – remove bold from label Yes
B No No No
C Yes Yes E Yes
D No No No
E Yes C Yes
Yes
F Yes Yes Yes
F
B
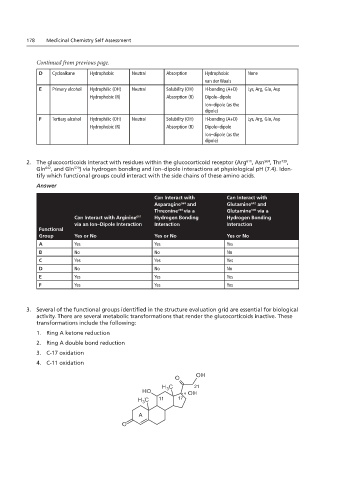
3. Several of the functional groups identified in the structure evaluation grid are essential for biological
D
A
activity. There are several metabolic transformations that render the glucocorticoids inactive. These
transformations include the following:
1. Ring A ketone reduction Hydrocortisone
2. Ring A double bond reduction
3. C-17 oxidation Question #3 structure needs to be replaced:
4. C-11 oxidation
21
11 17
A
1.18 and 2.18 – remove bold from label
E
A I C D O
H O I
OH
NH
I O 2
B I
L-Thyroxine