Page 19 - Medicinal Chemistry Self Assessment
P. 19
1.2
8
Medicinal Chemistry Self Assessment
1. For each of the drugs or experimental drugs shown below, identify all of the acidic and basic functional
groups.
2. Using any one of the acidic functional groups that you identified in question 1, provide an explana-
tion as to why the functional group is acidic. Also provide a similar type of analysis for any one of the
basic functional groups that you identified in question 1.
3. Using the structures from question 1, modify all of the acidic functional groups to show their ionized
forms and in the table below identify the normal pK range for the specific functional group.
a
Bromfenac
Drug Name Experimental oral anticoagulant Normal pK Range
Acidic Functional Group
a
Experimental Oral Anticoagulant
Bromfenac
Sorbinil
Experimental Antidiabetic Agent
4. Using the structures from question 1, modify all basic functional groups to show their ionized forms
and in the table below identify the normal pK range for the specific functional group.
Sorbinil
a
Experimental antidiabetic agent
Drug Name Basic Functional Group Normal pK Range
a
Experimental Oral Anticoagulant
Bromfenac
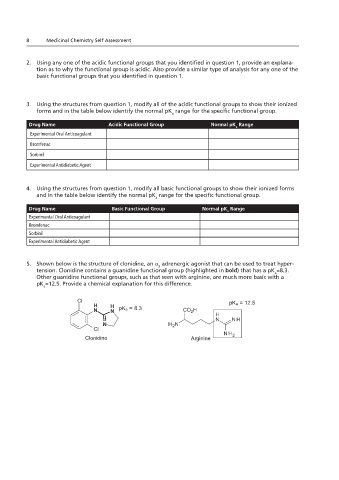
5. Shown below is the structure of clonidine, an D adrenergic agonist that can be used to treat hypertension.
Sorbinil
Experimental Antidiabetic Agent
Clonidine contains a guanidine functional group (highlighted in bold) that has a pKa of 8.3. Other guanidine
functional groups, such as that seen with arginine are much more basic with a pKa of 12.5. Provide a chemical
5. Shown below is the structure of clonidine, an α adrenergic agonist that can be used to treat hyper-
2
tension. Clonidine contains a guanidine functional group (highlighted in bold) that has a pK =8.3.
explanation for this difference. a
Other guanidine functional groups, such as that seen with arginine, are much more basic with a
pK =12.5. Provide a chemical explanation for this difference.
a
pK a = 12.5
pK a = 8.3
Clonidine Arginine
Page 1 of 2