Page 22 - Medicinal Chemistry Self Assessment
P. 22
Section 1 General Self Assessment
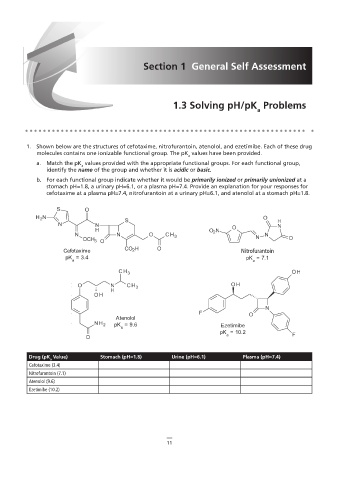
1.3 Solving pH/pK Problems
a
1. Shown below are the structures of cefotaxime, nitrofurantoin, atenolol, and ezetimibe. Each of these drug
1. Shown below are the structures of cefotaxime, nitrofurantoin, atenolol, and ezetimibe. Each of these drug
molecules contains one ionizable functional group. The pK values have been provided.
molecules contains one ionizable functional group. The pK a values have been provided.
a
a. Match the pK values provided with the appropriate functional groups. For each functional group,
b. For each functional group indicate whether it would be primarily ionized or primarily unionized at a
a
identify the name of the group and whether it is acidic or basic.
for cefotaxime at a plasma pH of 7.4, nitrofurantoin at a urinary pH of 6.1, a stomach pH of 1.8.
b. For each functional group indicate whether it would be primarily ionized or primarily unionized at a
stomach pH=1.8, a urinary pH=6.1, or a plasma pH=7.4. Provide an explanation for your responses for
cefotaxime at a plasma pH=7.4, nitrofurantoin at a urinary pH=6.1, and atenolol at a stomach pH=1.8.
Cefotaxime Nitrofurantoin
Nitrofurantion
pK = 3.4 pK = 7.1
a a
Atenolol
pK = 9.6 Ezetimibe
a
pK = 10.2
a
Drug (pK Value) Stomach (pH=1.8) Urine (pH=6.1) Plasma (pH=7.4)
a
3. Shown below is the structure of natamycin. It contains two functional groups that could be potentially ionized.
Cefotaxime (3.4)
Nitrofurantoin (7.1)
The pK a values for natamycin are 4.6 and 8.4.
Atenolol (9.6)
Ezetimibe (10.2)
O OH
O OH
H C O OH O
3
COOH
11
O O CH 3
Natamycin
H O OH
NH
2
Page 1 of 2