Page 25 - Medicinal Chemistry Self Assessment
P. 25
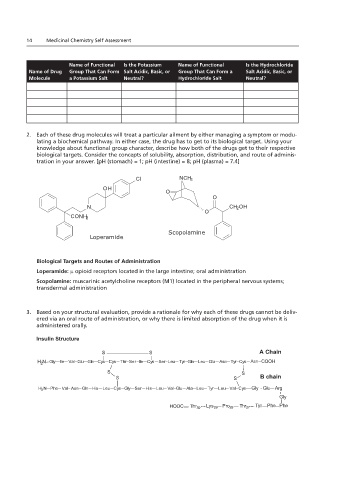
14 Medicinal Chemistry Self Assessment
Name of Functional Is the Potassium Name of Functional Is the Hydrochloride
Name of Drug Group That Can Form Salt Acidic, Basic, or Group That Can Form a Salt Acidic, Basic, or
Molecule a Potassium Salt Neutral? Hydrochloride Salt Neutral?
2. Each of these drug molecules will treat a particular ailment by either managing a symptom or
modulating a biochemical pathway. In either case, the drug has to get to its biological target. Using your
knowledge about functional group character, describe how both of the drugs get to their respective
2. Each of these drug molecules will treat a particular ailment by either managing a symptom or modu-
biological targets. Consider the concepts of solubility, absorption, distribution, and route of administration
lating a biochemical pathway. In either case, the drug has to get to its biological target. Using your
knowledge about functional group character, describe how both of the drugs get to their respective
in your answer. [pH (stomach) = 1; pH (intestine) = 8; pH (plasma) = 7.4]
biological targets. Consider the concepts of solubility, absorption, distribution, and route of adminis-
tration in your answer. [pH (stomach) = 1; pH (intestine) = 8; pH (plasma) = 7.4]
Cl NCH 3
OH
O
O
N CH 2 OH
O
CONH 2
Scopolamine
Loperamide
Biological Targets and Routes of Administration
3. Based on your structural evaluation, provide a rationale for why each of these drugs cannot be
Loperamide: µ opioid receptors located in the large intestine; oral administration
delivered via an oral route of administration, or why there is limited absorption of the drug when it is
Scopolamine: muscarinic acetylcholine receptors (M1) located in the peripheral nervous systems;
transdermal administration
administered orally.
3. Based on your structural evaluation, provide a rationale for why each of these drugs cannot be deliv-
ered via an oral route of administration, or why there is limited absorption of the drug when it is
administered orally.
Insulin Structure
PO 3 Na 2
S S H 2 N PO 3 Na 2 A Chain
OH
H 2 N Gly Ile ValGlu GlnCys CysThr SerIle CysSer LeuTyr GlnLeu GluAsn TyrCys Asn COOH
S S
S Alendronate S B chain
H 2 NPhe ValAsn GlnHis LeuCys GlySer His Leu ValGlu AlaLeu Tyr Leu ValCys GlyGlu Arg
Insulin
Gly
HOOC Thr 30 Lys 29 Pro 28 Thr 27 Tyr Phe Phe