Page 195 - Medicinal Chemistry Self Assessment
P. 195
184 Medicinal Chemistry Self Assessment
Continued from previous page.
C
Hydrophobic
Halogenated
1.18 and 2.18 – remove bold from label Neutral Absorption Dipole–dipole None
aromatic hydro- Ion–dipole (as the
carbon dipole)
Hydrophobic
van der Waals
π-π Stacking
D Primary amine Hydrophilic (NH ) Basic Solubility (NH ) Ion–dipole (as the ion) None
2 2
Hydrophobic (R) pK =9–11 Absorption (R) Ionic
a
E Carboxylic acid Hydrophilic (CO H) Acidic Solubility (CO H) Ion–dipole (as the ion) None
2
Tri-iodothyronine Hydrophobic (R) pK =2–5 Absorption (R) 2 Ionic
a
1. Conduct a structural your answers to the questions that follow.
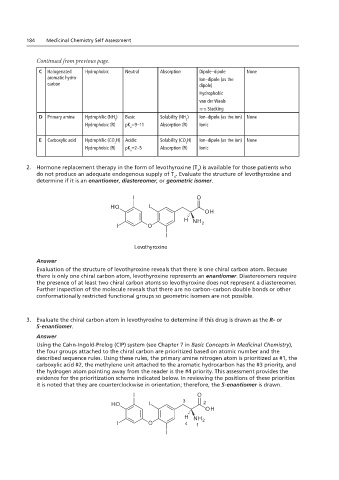
2. Hormone replacement therapy in the form of levothyroxine (T ) is available for those patients who
1.18 and 2.18 – remove bold from label E 4
do not produce an adequate endogenous supply of T . Evaluate the structure of levothyroxine and
determine if it is an enantiomer, diastereomer, or geometric isomer.
4
A C D
O
I O
H 2 N OH I
H H O OH
B H NH
I O 2
OH L-Thyroxine <DAVID: please change caption to Levothyroxine>
I
L-Tyrosine Levothyroxine
2. Hormone replacement, diastereomer, or geometric isomer.
Answer
Evaluation of the structure of levothyroxine reveals that there is one chiral carbon atom. Because
there is only one chiral carbon atom, levothyroxine represents an enantiomer. Diastereomers require
the presence of at least two chiral carbon atoms so levothyroxine does not represent a diastereomer.
Further inspection of the molecule reveals that there are no carbon–carbon double bonds or other
conformationally restricted functional groups so geometric isomers are not possible.
3. Evaluate the chiral carbon atom in levothyroxine to determine if this drug is drawn as the R- or
Levothyroxine
S-enantiomer.
Answer
Using the Cahn-Ingold-Prelog (CIP) system (see Chapter 7 in Basic Concepts in Medicinal Chemistry),
3. Evaluate the chiral carbon atom this drug is drawn as the R- or S-enantiomer.
the four groups attached to the chiral carbon are prioritized based on atomic number and the
described sequence rules. Using these rules, the primary amine nitrogen atom is prioritized as #1, the
Answer:
carboxylic acid #2, the methylene unit attached to the aromatic hydrocarbon has the #3 priority, and
the hydrogen atom pointing away from the reader is the #4 priority. This assessment provides the
Using the; therefore, the S-enantiomer is drawn.
evidence for the prioritization scheme indicated below. In reviewing the positions of these priorities
it is noted that they are counterclockwise in orientation; therefore, the S-enantiomer is drawn.
3 2
4 1