Page 200 - Medicinal Chemistry Self Assessment
P. 200
Section 4 Whole Molecule Drug Evaluation
Answers
2.19 Lidocaine
As a sodium channel blocker lidocaine has found therapeutic use both as a local anesthetic and as a Class IB antiarrhythmic
agent. As an anesthetic, this agent demonstrates rapid onset of action (acts quickly) and a longer duration of action
(lasts longer) than most amino ester-type local anesthetics. The most frequently observed side effects are changes in
the central nervous system (CNS) (e.g., dizziness, lightheadedness, and tinnitus). Lidocaine is extensively metabolized
by the CYP1A2 isozymes to a variety of metabolites.
1. Conduct a the in the grid to inform your answers to some of the questions that follow.
1. Conduct a complete structural evaluation of lidocaine, place your answers in the grid provided, and then
use the evaluation information in the grid to inform your answers to some of the questions that follow.
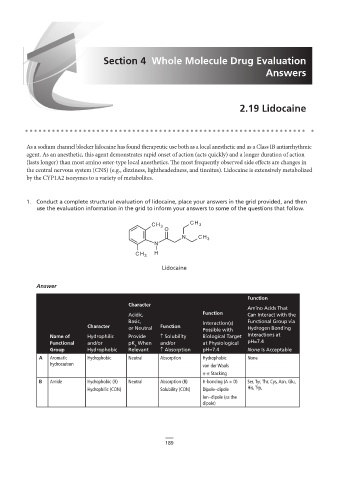
CH 3 CH 3
O
N CH 3
N
CH 3 H
Lidocaine
Lidocaine
Answer
Answer:
Function
Character
Amino Acids That
Acidic, Function Can Interact with the
A
Basic, C Interaction(s) Functional Group via
Character or Neutral Function Possible with Hydrogen Bonding
D
Name of Hydrophilic Provide ↑ Solubility Biological Target Interactions at
Functional and/or pK When and/or at Physiological pH=7.4
a
Group Hydrophobic Relevant ↑ Absorption pH=7.4 None Is Acceptable
A Aromatic Hydrophobic Neutral B Hydrophobic None
Absorption
hydrocarbon van der Waals
π-π Stacking
Lidocaine
B Amide Hydrophobic (R) Neutral Absorption (R) H-bonding (A + D) Ser, Tyr, Thr, Cys, Asn, Glu,
Hydrophilic (CON) Solubility (CON) Dipole–dipole His, Trp,
Ion–dipole (as the
2. Based on the information in the dipole)
3. Local anesthetics that have.
189